Childhood Trauma's Long-Term Impact on Mental Health and Pain
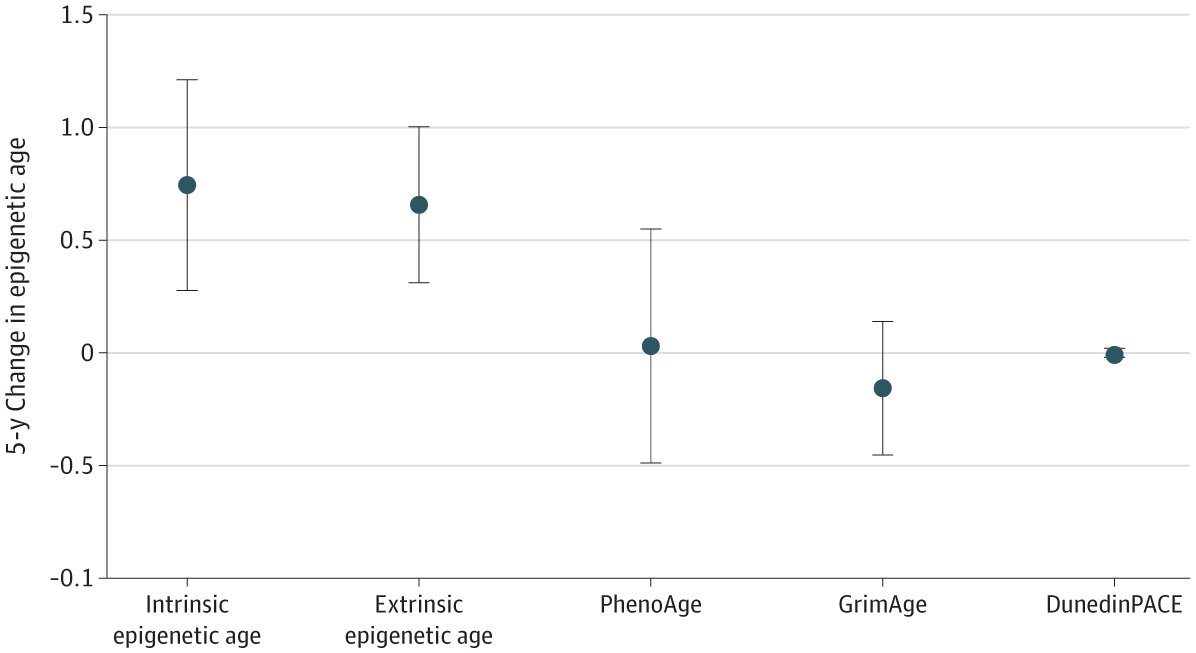
A study from the University of Aberdeen found that childhood trauma, especially multiple adverse experiences, is strongly linked to mental health issues and chronic pain at age 50, with women being more affected than men, highlighting the importance of early intervention and prevention.