Hibernation for Long Spaceflights Closer to Reality, Say Scientists.
TL;DR Summary
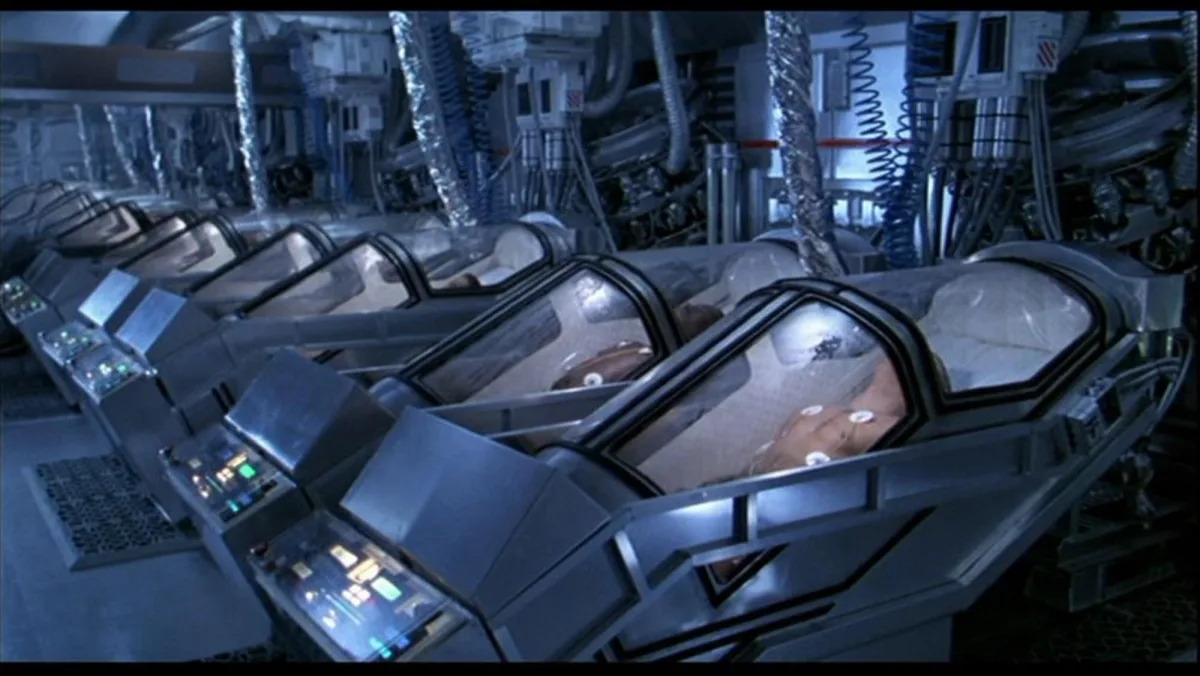
The first hibernation studies with human subjects could be feasible within a decade, according to a European Space Agency (ESA) researcher. Hibernating on a year-long trip to Mars would not just prevent boredom in a tiny space capsule; it would also save mission cost, as the hibernating crew members wouldn't need to eat or drink and would even require far less oxygen than those awake. Research in animals suggests that bodies of hibernating astronauts might waste away much less than the bodies of those awake in microgravity.
Reading Insights
Total Reads
0
Unique Readers
9
Time Saved
7 min
vs 8 min read
Condensed
94%
1,496 → 87 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Yahoo News