"Resolving the Mystery: Understanding the Universe's Expansion"
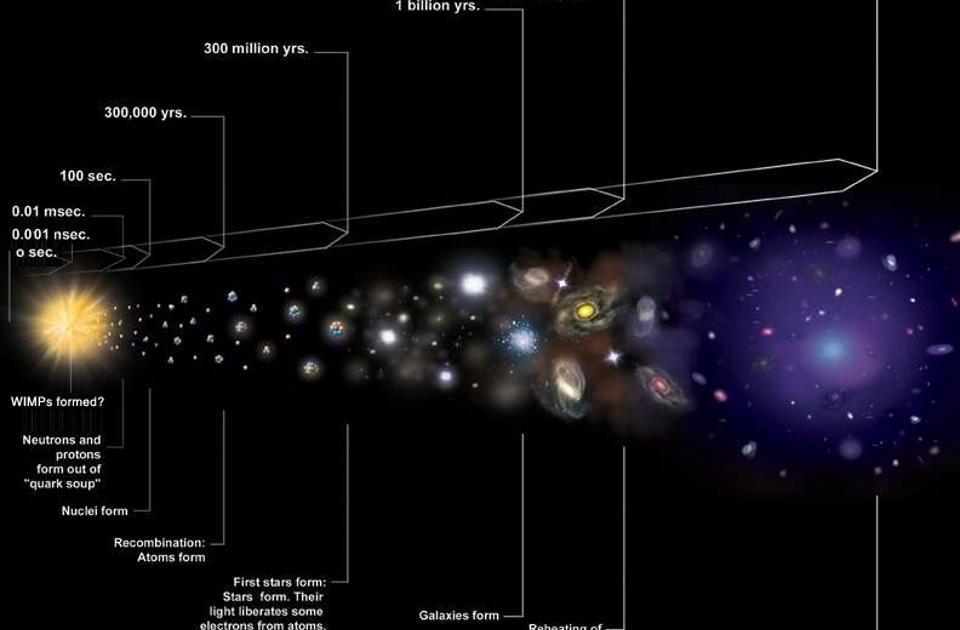
The expansion of the Universe does not break the speed of light. The speed of the expansion of space is not a constant value, but rather varies depending on the distance of the object being observed. The redshift observed in light from distant objects is caused by the expanding Universe, gravitational potential differences, and relative motion between the source and the observer. The expansion rate is typically expressed in terms of kilometers-per-second-per-megaparsec, and current measurements fall within a range of 67 to 74 km/s/Mpc. Objects closer than 14 billion light-years are receding from us at speeds slower than light, while those farther away are receding faster than light due to the expanding space between them.
- No, the expanding Universe doesn't break the speed of light Big Think
- Hubble and Webb disagree over Hubble tension Sky at Night Magazine
- How fast is the universe expanding? New data keeps mystery open The Hindu
- Astro Brief: Expansion of the Universe KSMU Radio
- One of the biggest mysteries of cosmology may finally be solved New Scientist
Reading Insights
0
1
14 min
vs 15 min read
96%
2,981 → 115 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Big Think