Brain's Omega-3 Fatty Acid Acquisition Model Developed by Researchers.
TL;DR Summary
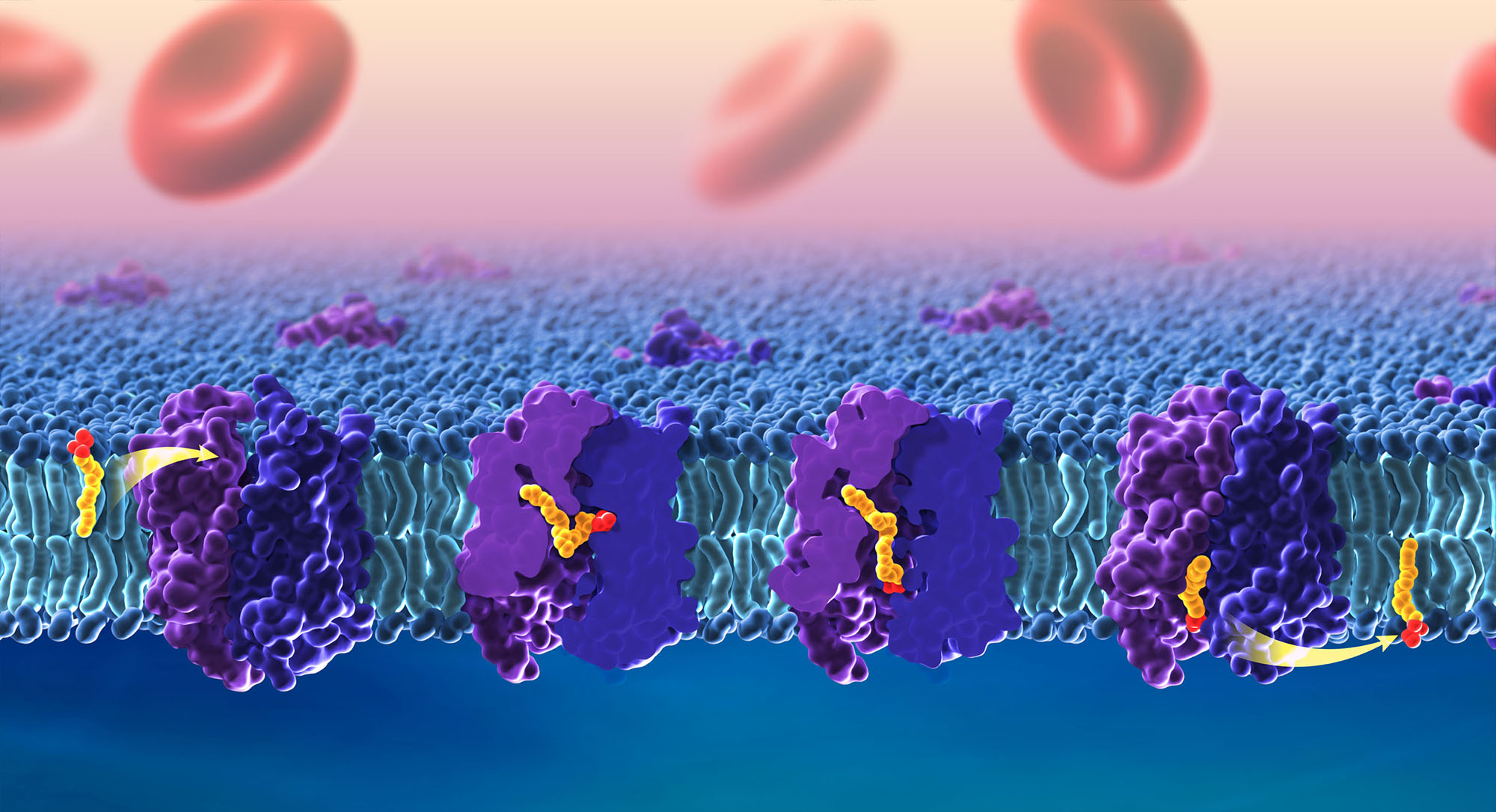
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health and colleagues have developed a zebrafish model that provides new insight into how the brain acquires essential omega-3 fatty acids, including docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and linolenic acid (ALA). Their findings have the potential to improve understanding of lipid transport across the blood-brain barrier and of disruptions in this process that can lead to birth defects or neurological conditions. The model may also enable researchers to design drug molecules that are capable of directly reaching the brain.
Researchers develop model for how the brain acquires essential omega-3 fatty acids National Institutes of Health (.gov)View Full Coverage on Google News
Reading Insights
Total Reads
0
Unique Readers
0
Time Saved
3 min
vs 4 min read
Condensed
86%
606 → 83 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on National Institutes of Health (.gov)