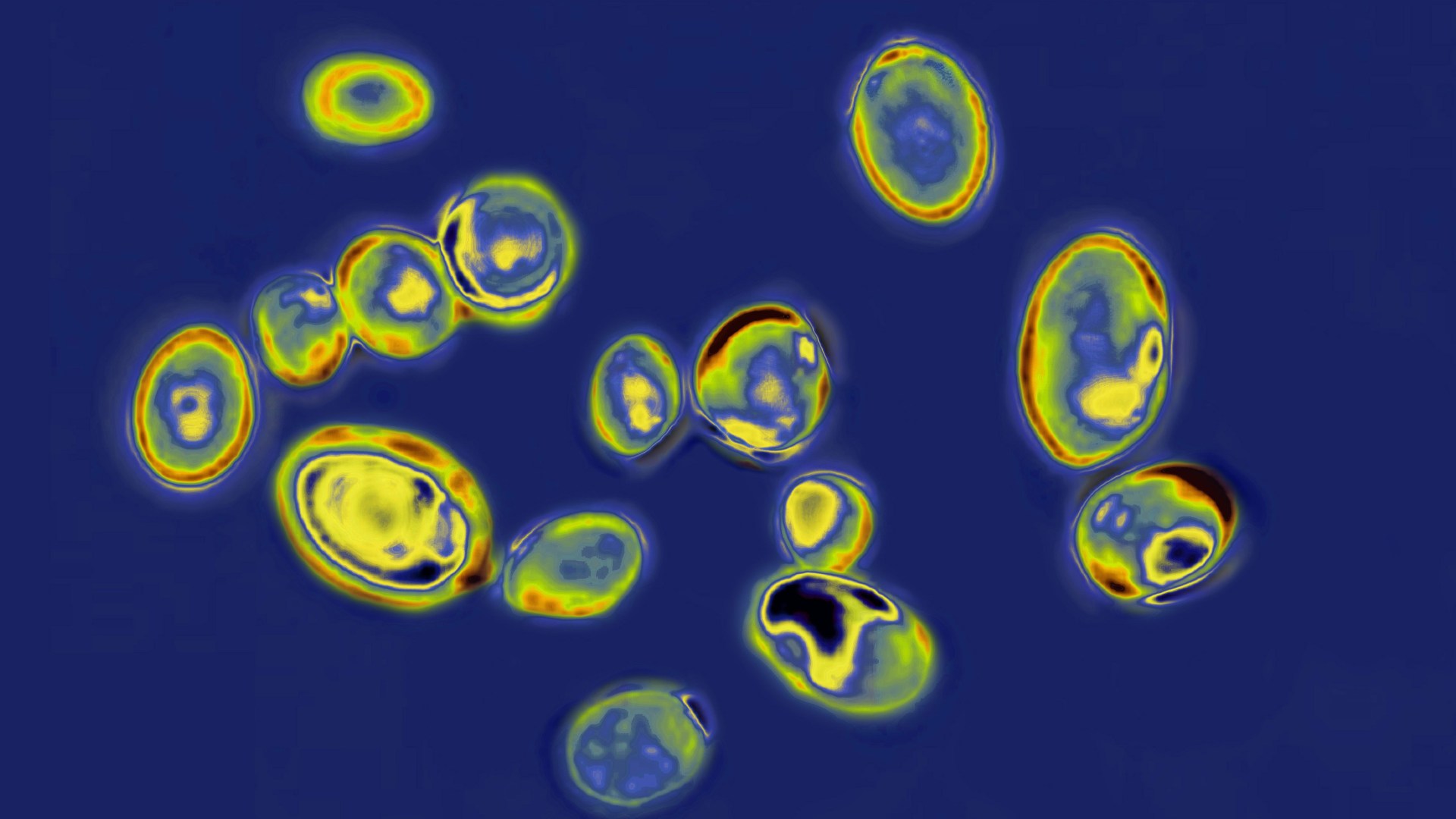
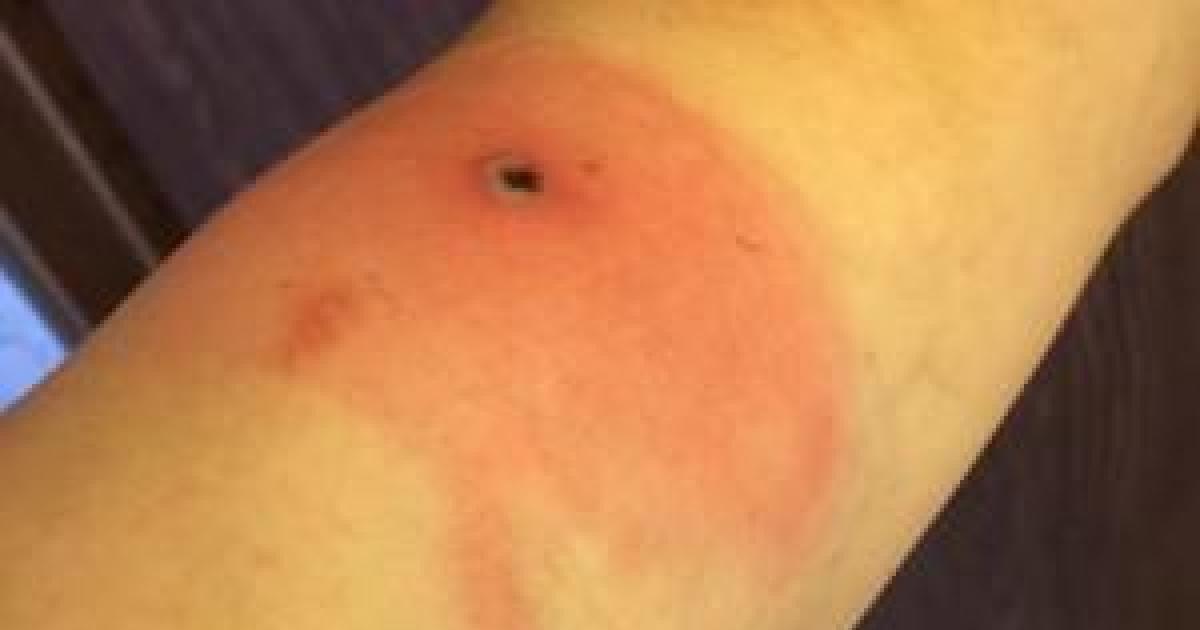
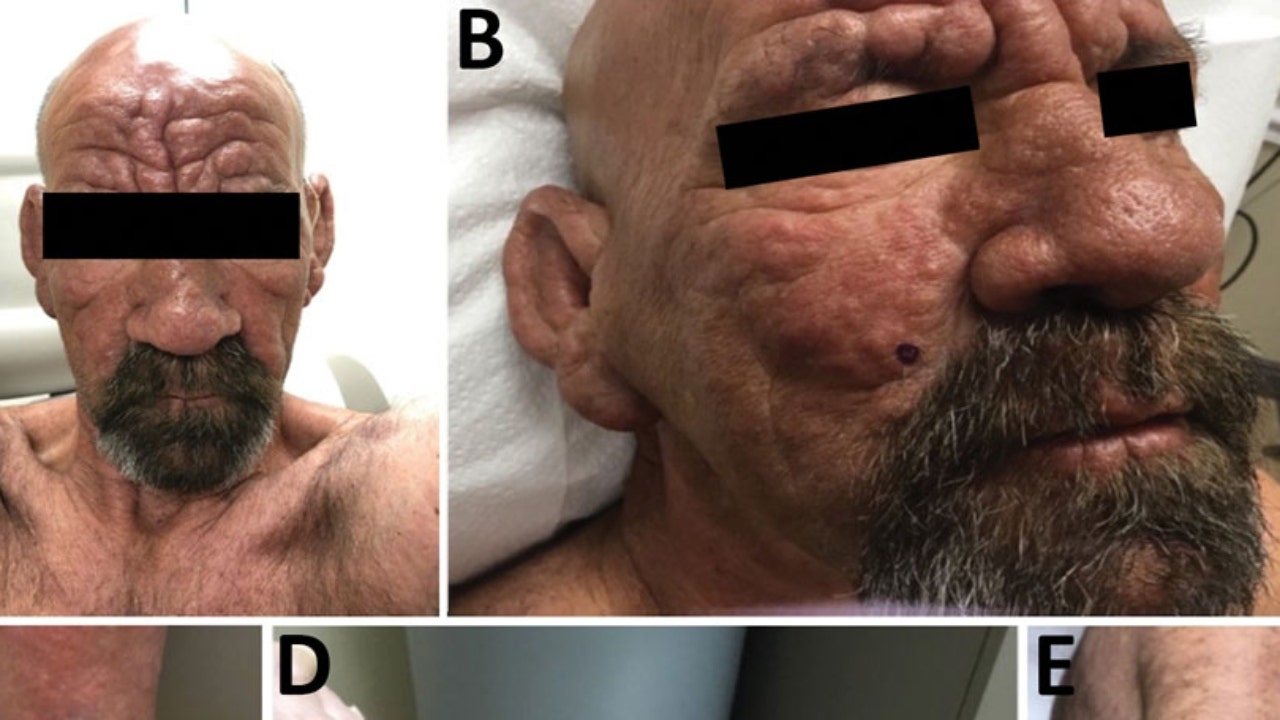
Early-Season Human Plague Transmission from Infected Cat in Oregon, January 2024
A rare early-season human case of plague in Oregon in January 2024 was transmitted from an infected cat, highlighting the need for year-round public health awareness and veterinary precautions due to changing environmental factors and climate conditions that may extend flea activity and plague transmission seasons.