"China Aims for 5% Economic Growth, Promises Support for Consumers and Developers"
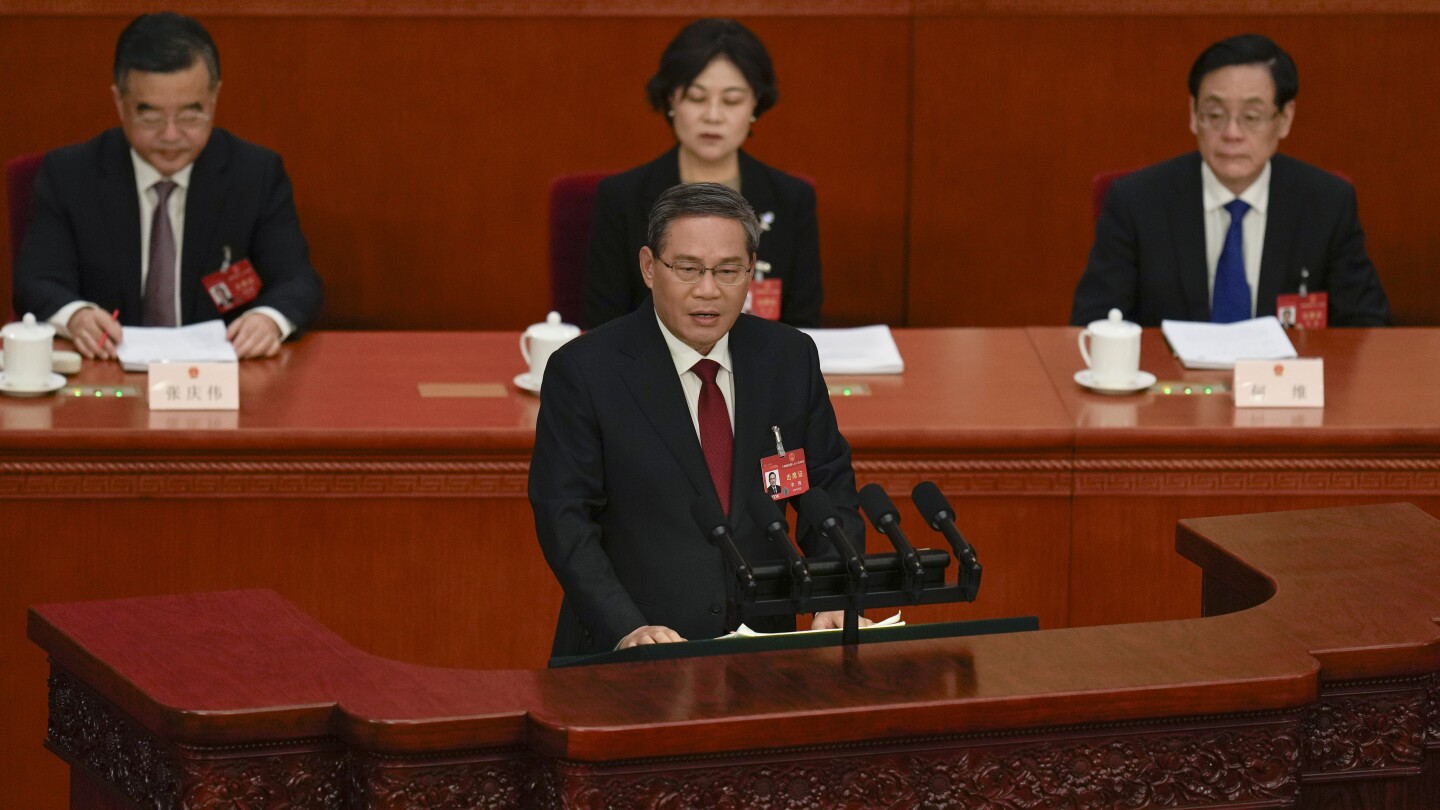
China aims for 5% economic growth this year, with plans to boost spending on technology, military, and the economy, but no major stimulus package. Premier Li Qiang acknowledged the challenges, including a real estate slump and overcapacity in some industries. The government plans to issue long-term bonds to boost growth and address housing market issues. The draft budget includes a 7.2% rise in defense spending. China's economy grew at a 5.2% pace last year, but replicating this growth will be difficult. The government emphasizes the need to raise consumer spending and provide support for local governments facing economic difficulty.