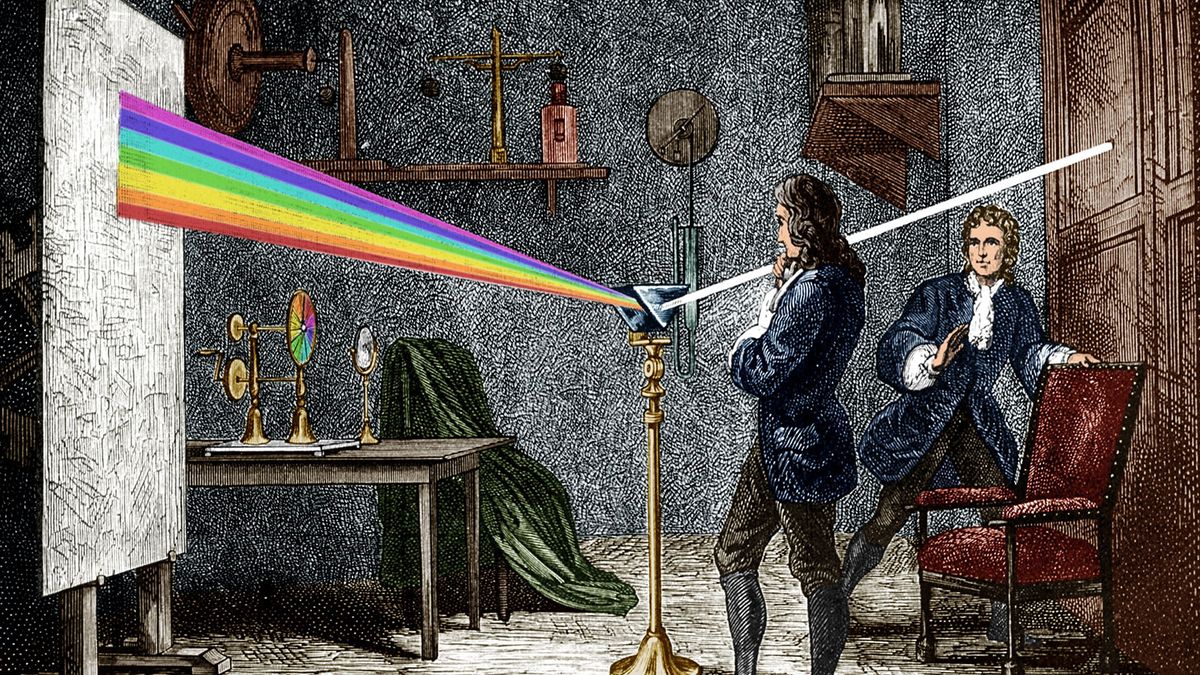
Unveiling the Mystery of Light: Isaac Newton's Refraction Experiments
Isaac Newton's experiment with prisms in 1666 revolutionized our understanding of light, revealing that the colors of the rainbow are inherent in white light itself and that prisms simply separate them out through refraction. Newton's findings, published in his book Opticks in 1704, explained the nature of light, the formation of rainbows, and the defects of lenses. Despite initial criticism, his experiments have stood the test of time and continue to illuminate the unknown.



