"Black Hole Spaghettifying a Star: Rare Discovery Recorded by Hawaiʻi Astronomers"
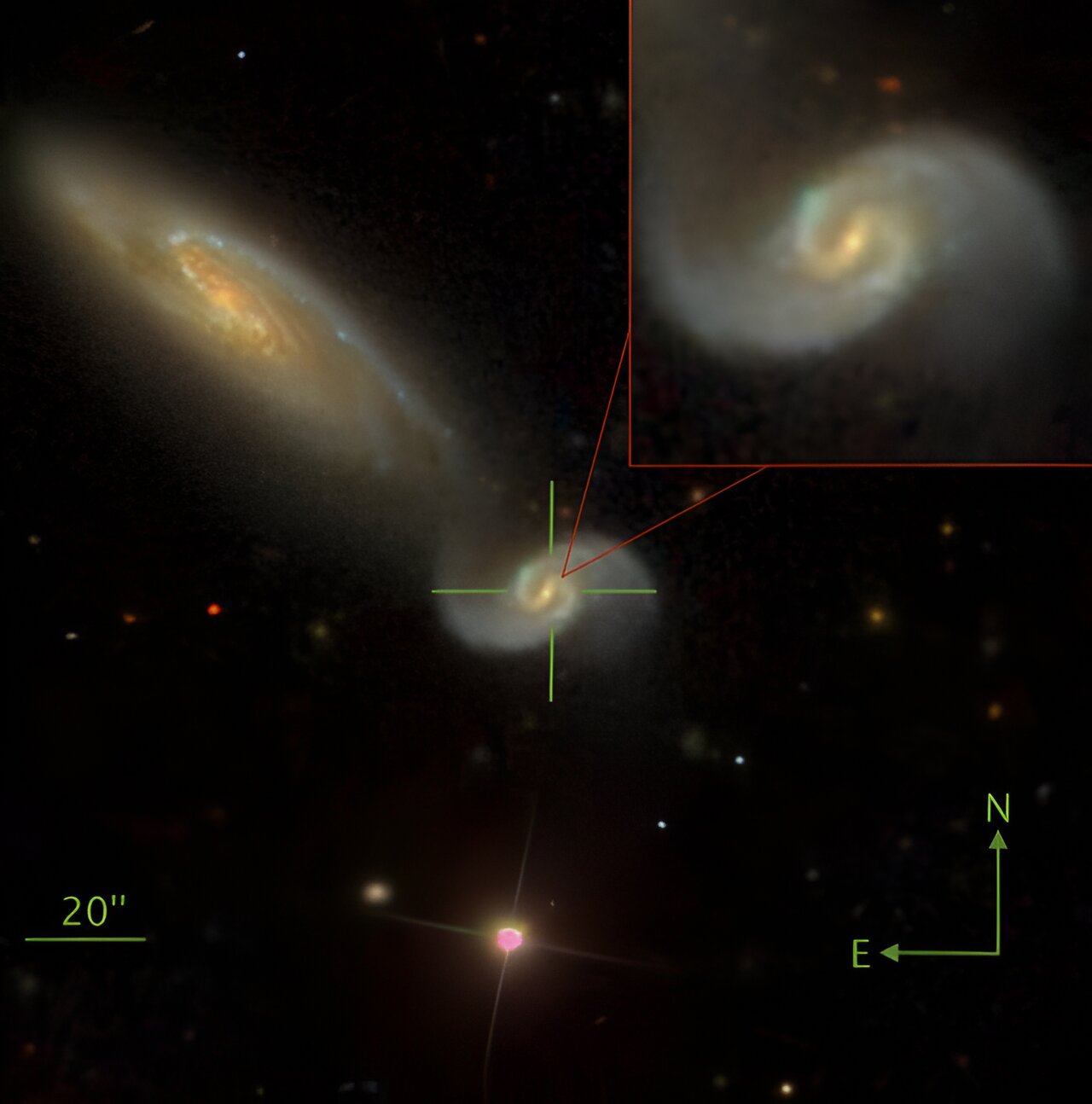
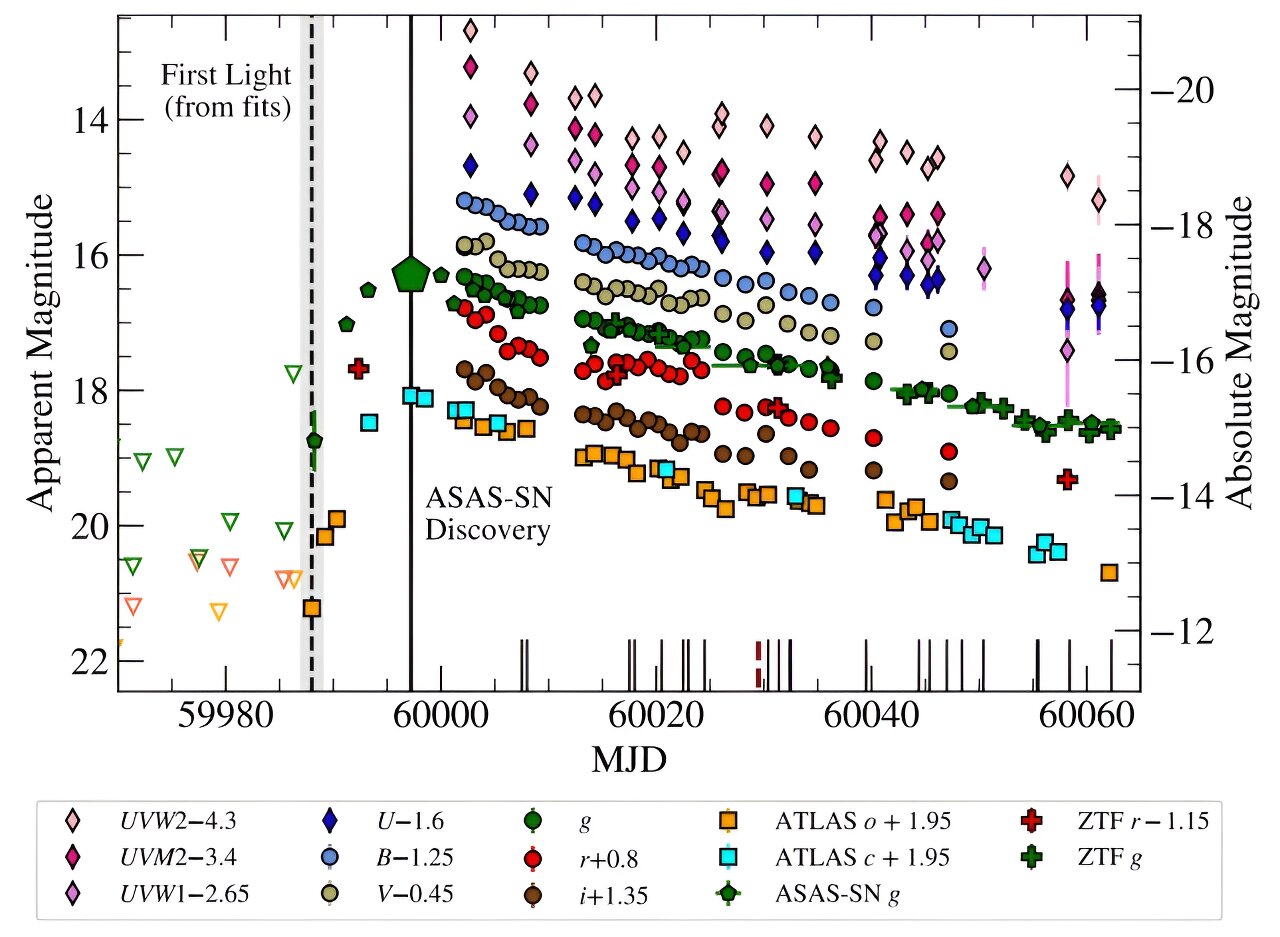
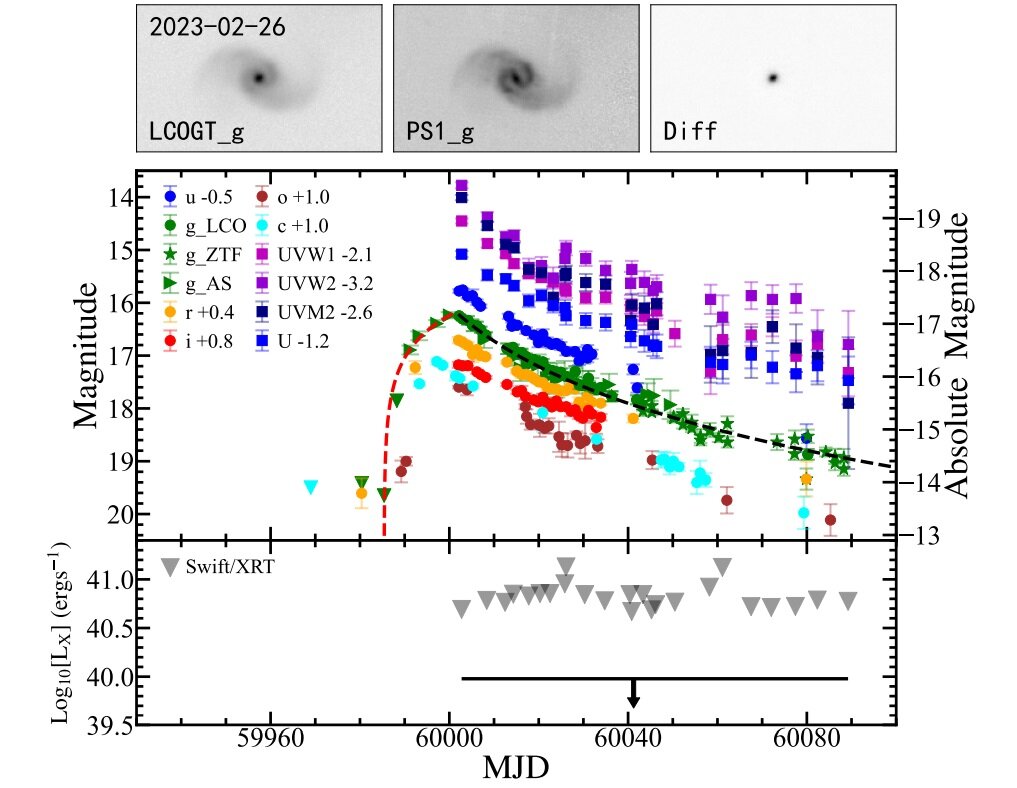
Astronomers have observed a supermassive black hole tearing apart and consuming a star in a tidal disruption event (TDE) remarkably close to Earth, in the galaxy NGC 3799. This rare event, designated ASASSN-23bd, provides valuable insights into the growth of supermassive black holes. The TDE brightened and dimmed over just 15 days, making it twice as fast as other TDEs and producing less energy, placing it in a category of "low luminosity and fast TDEs." The findings are set to be published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.