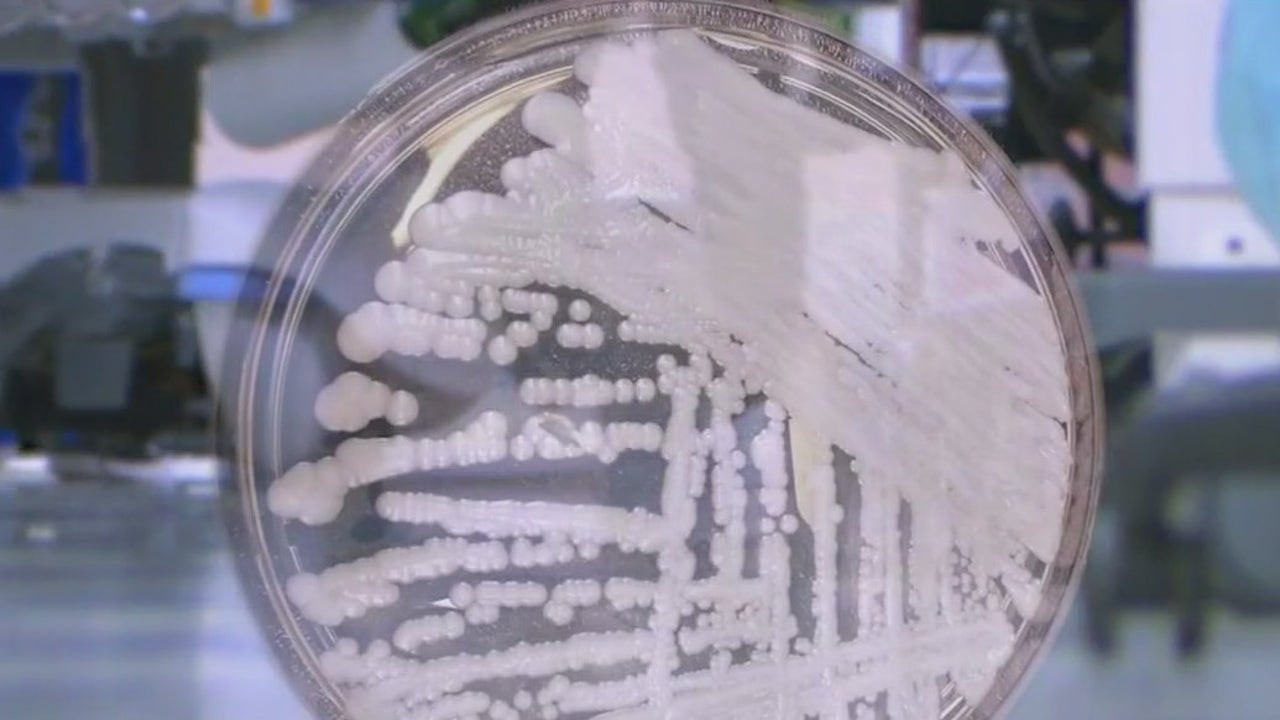
"Mutation of Multi-Drug Resistant Bacteria on ISS Driven by Space Environment"
NASA-funded research reveals that multi-drug resistant strains of the bacterium Enterobacter bugandensis, isolated from the International Space Station (ISS), have mutated to become genetically and functionally distinct from their Earth counterparts, persisting and coexisting with other microorganisms in the extreme environment of the ISS. This study sheds light on microbial dynamics in closed human-built environments, providing insights for effective preventative measures for astronaut health in space.