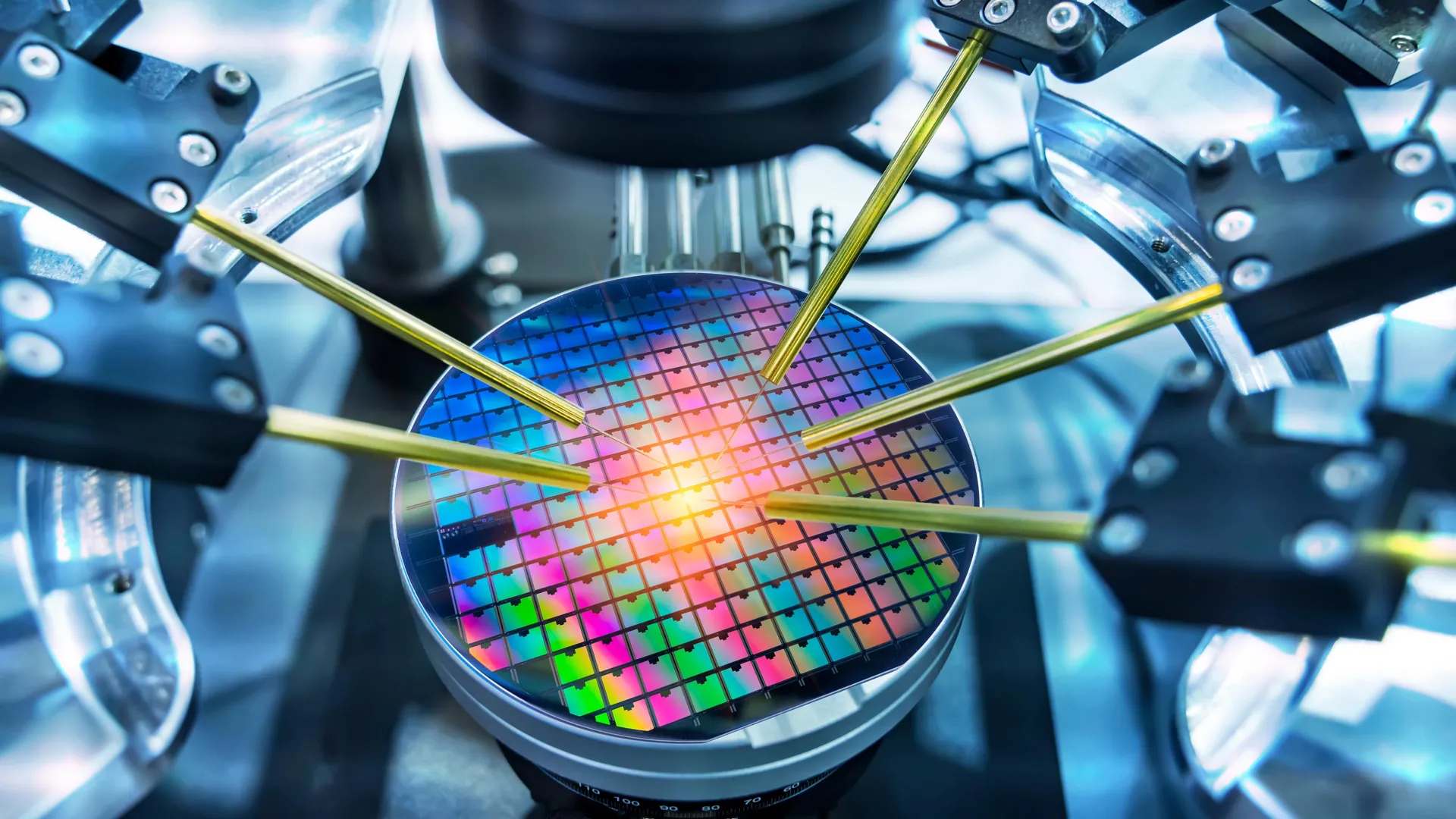
Johns Hopkins Develops Technique to Create Sub-10nm Microchips
Researchers at Johns Hopkins have developed new materials and a process called chemical liquid deposition to create ultra-small, invisible circuits on microchips, potentially revolutionizing the production of smaller, faster, and more affordable electronics in the future.