"Galileo Galilei: Shaping Our Understanding of the Stars"
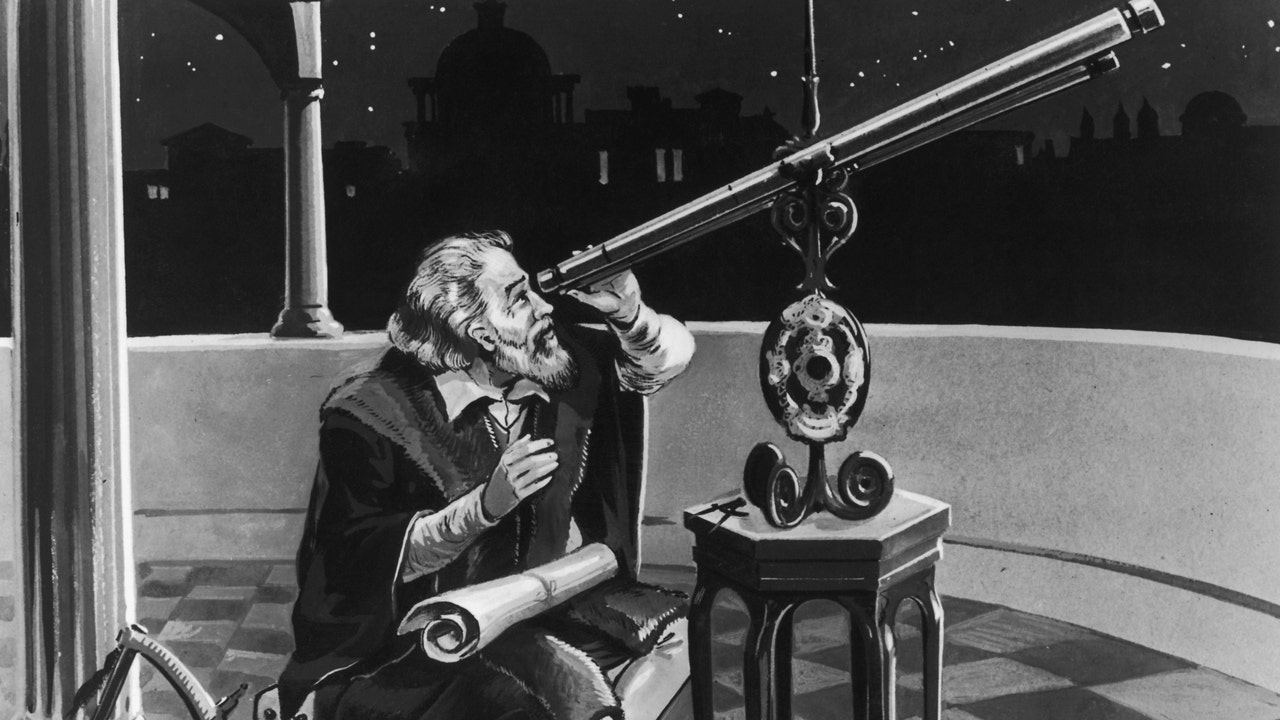
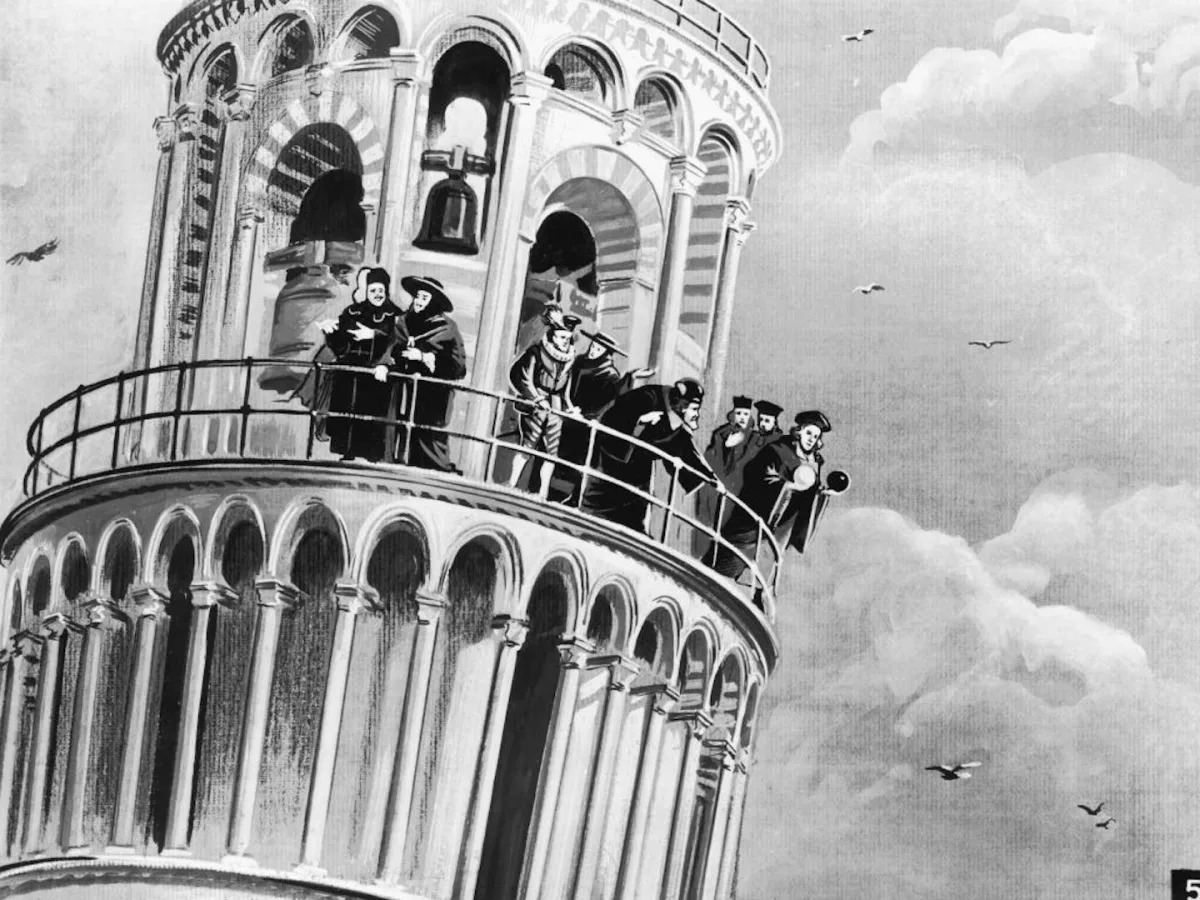
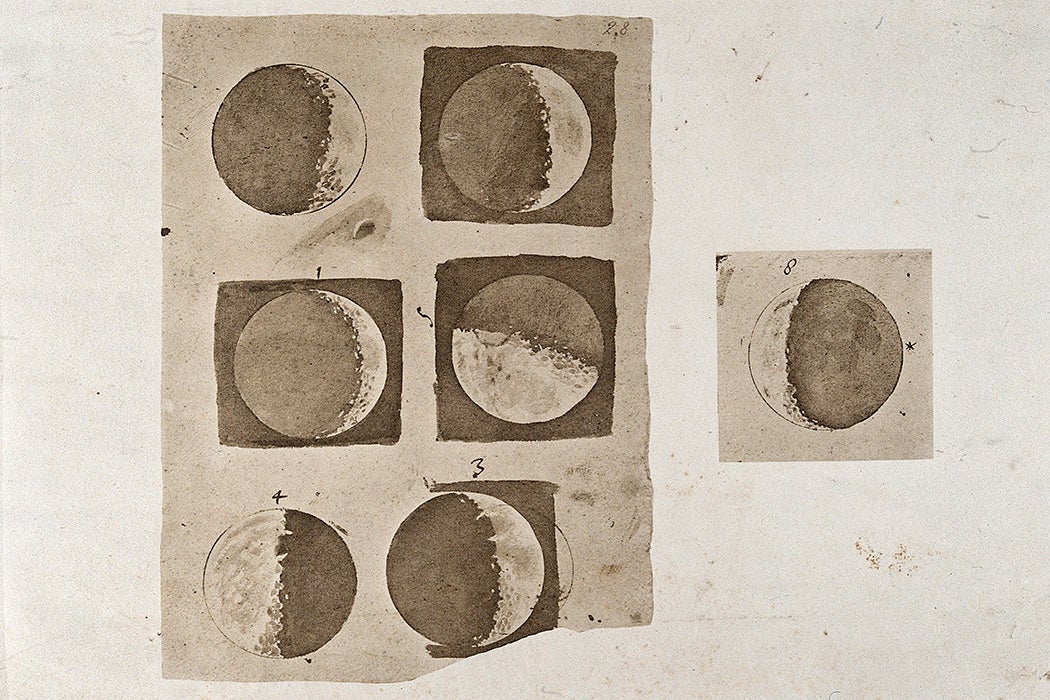
Galileo Galilei, an Italian philosopher, made groundbreaking contributions to astronomy during the Renaissance era, including the discovery of Jupiter's moons and sunspots. His advocacy for the Copernican theory and belief in heliocentrism led to a confrontation with the Catholic Church, resulting in his house arrest. Despite persecution, Galileo's legacy as a pioneer in physics, mathematics, and astronomy endures, shaping our understanding of the universe for centuries to come.