"Dietitian's Verdict: Diet Coke vs. Coke Zero - Which is Healthier?"
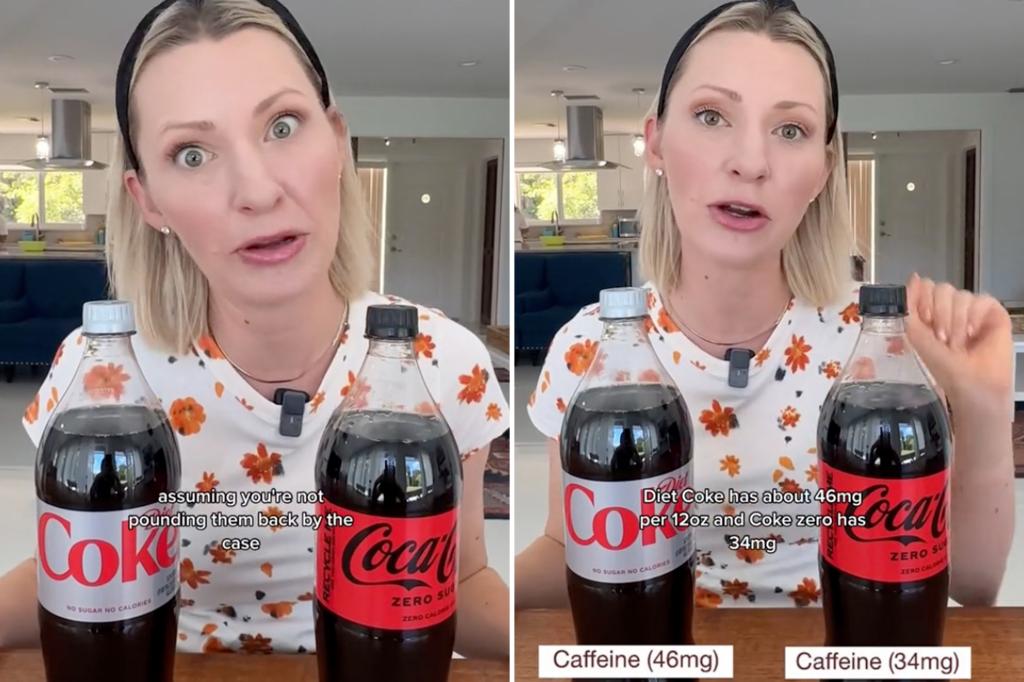
A Toronto-based registered dietitian compared the healthfulness of Diet Coke and Coke Zero, noting that both contain aspartame and caffeine, but Coke Zero also includes acesulfame potassium. While both sweeteners are FDA-approved, concerns have been raised about their potential health risks. The dietitian advised moderation and emphasized that diet sodas should be treated no differently than regular soda, cautioning that artificial sweeteners may trigger cravings for sweets and increase insulin levels over time.




