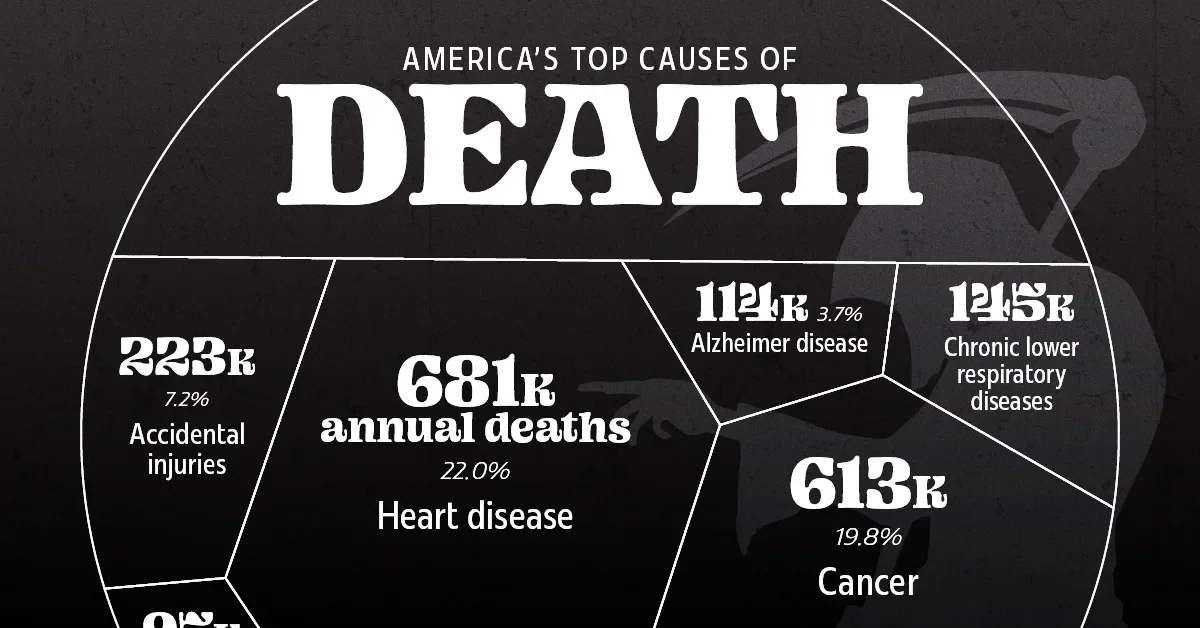
How to Survive the Top 10 Causes of Death Among Older Americans
The article highlights that 1.7 million older Americans die annually from top causes, and offers tips on how to improve survival through health awareness, preventive measures, and lifestyle changes.