"Record-breaking Ozone Hole in Antarctica Raises Concerns, Scientists Warn"
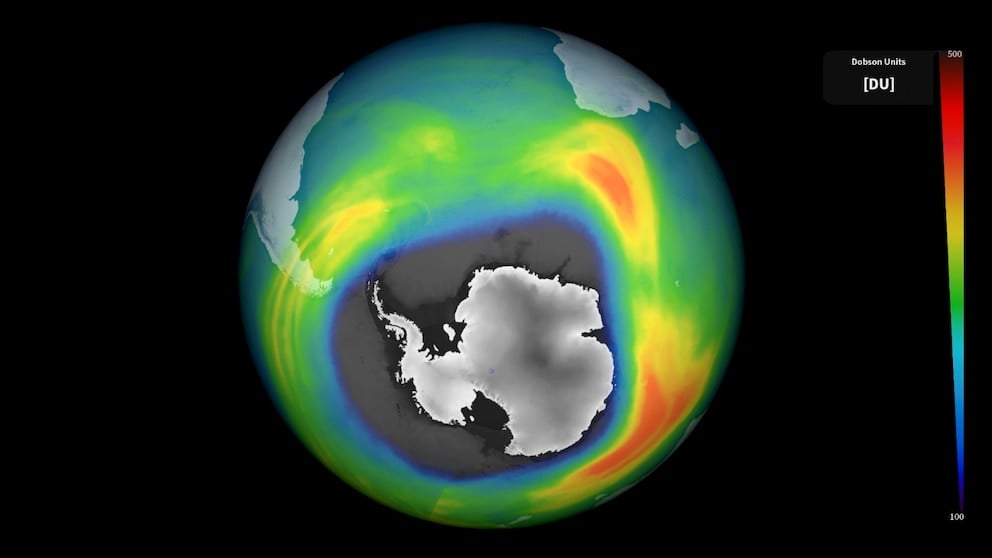
The annual ozone hole over Antarctica has grown to near-record size, measuring 26 million square kilometers, according to satellite imaging from Copernicus. The ozone hole, caused by ozone-depleting substances and specific regional conditions, typically reaches maximum depletion between mid-September and mid-October. This year, it started early and has rapidly expanded since mid-August, making it one of the largest on record. The size of the ozone hole is influenced by the strength of a wind band around Antarctica. The ozone layer is expected to recover within decades, but the unusual behavior in 2023 may be linked to the Tongan underwater volcano eruption in January 2022. The Montreal Protocol, which phased out ozone-depleting substances, has played a crucial role in addressing this issue.
Reading Insights
0
1
2 min
vs 3 min read
72%
426 → 121 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on ABC News