Astronaut Brains Shift in Space, Study Finds
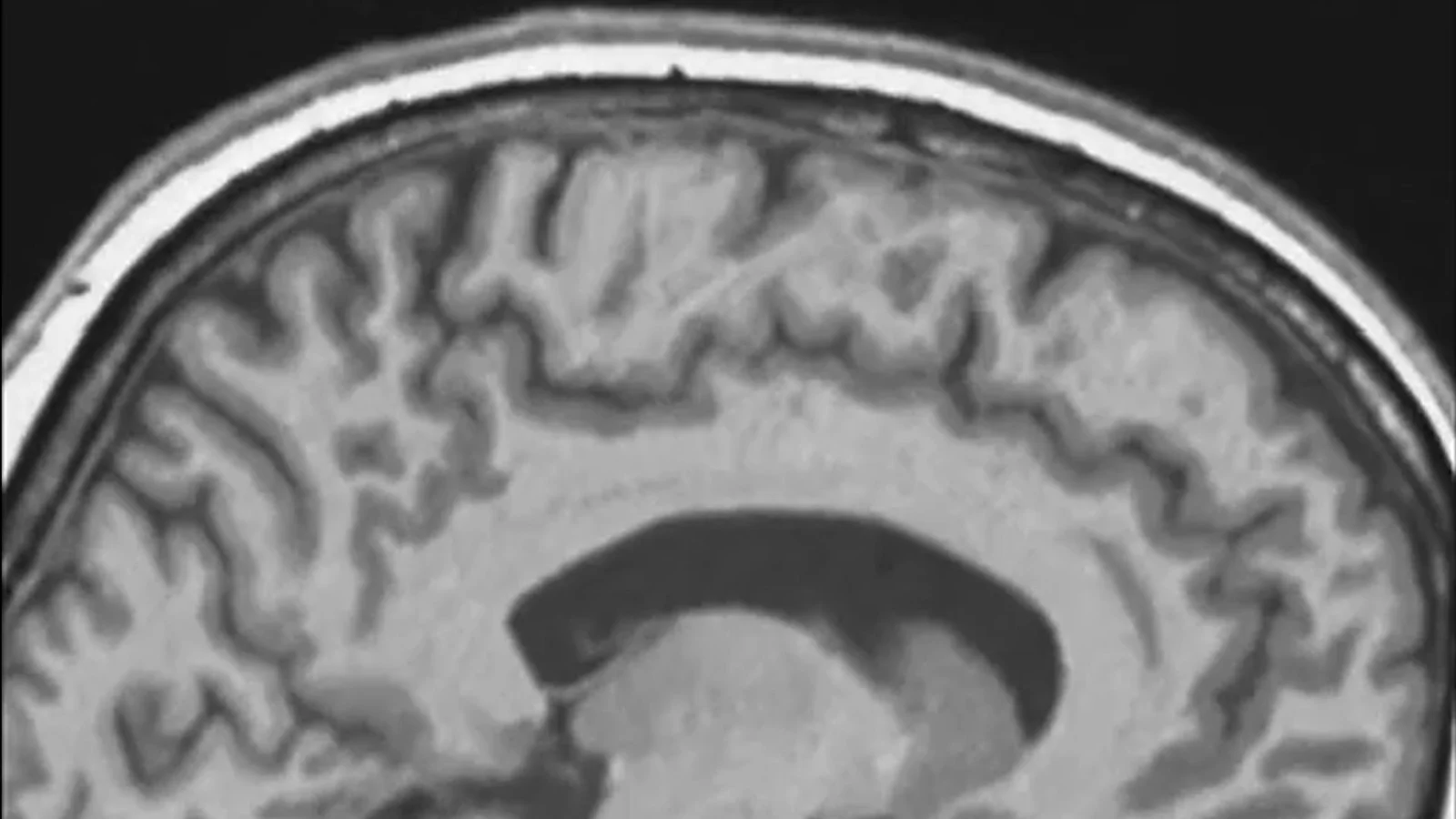
A MIT-led study analyzed MRI scans from 26 astronauts and 24 non-astronauts, finding that extended spaceflight consistently shifts the brain backward and upward inside the skull and alters its pitch. Some changes persist for months after returning to Earth, and the brain regions linked to balance and spatial orientation are affected. The research, which also compared spaceflight data to a bed-rest “microgravity analog,” suggests broad neuroanatomical effects from microgravity but notes limitations like small sample sizes and variability in mission duration. The team calls for larger, longer studies to understand onset, evolution, and recovery of these brain shifts.
- 'Backward and upward and tilted': Spaceflight causes astronauts' brains to shift inside their skulls Space
- Astronauts' brains change shape and position after time in space, study finds NBC News
- Spending Time in Space Can Change an Astronaut's Brain Shape and Position, According to Study People.com
- Spaceflight causes astronauts' brains to shift, stretch and compress in microgravity Phys.org
- New study finds astronauts' brains change after space travel Sky News
Reading Insights
0
4
45 min
vs 46 min read
99%
9,103 → 98 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Space