Air Pollution Study Reveals Improved Breathing Conditions Worldwide
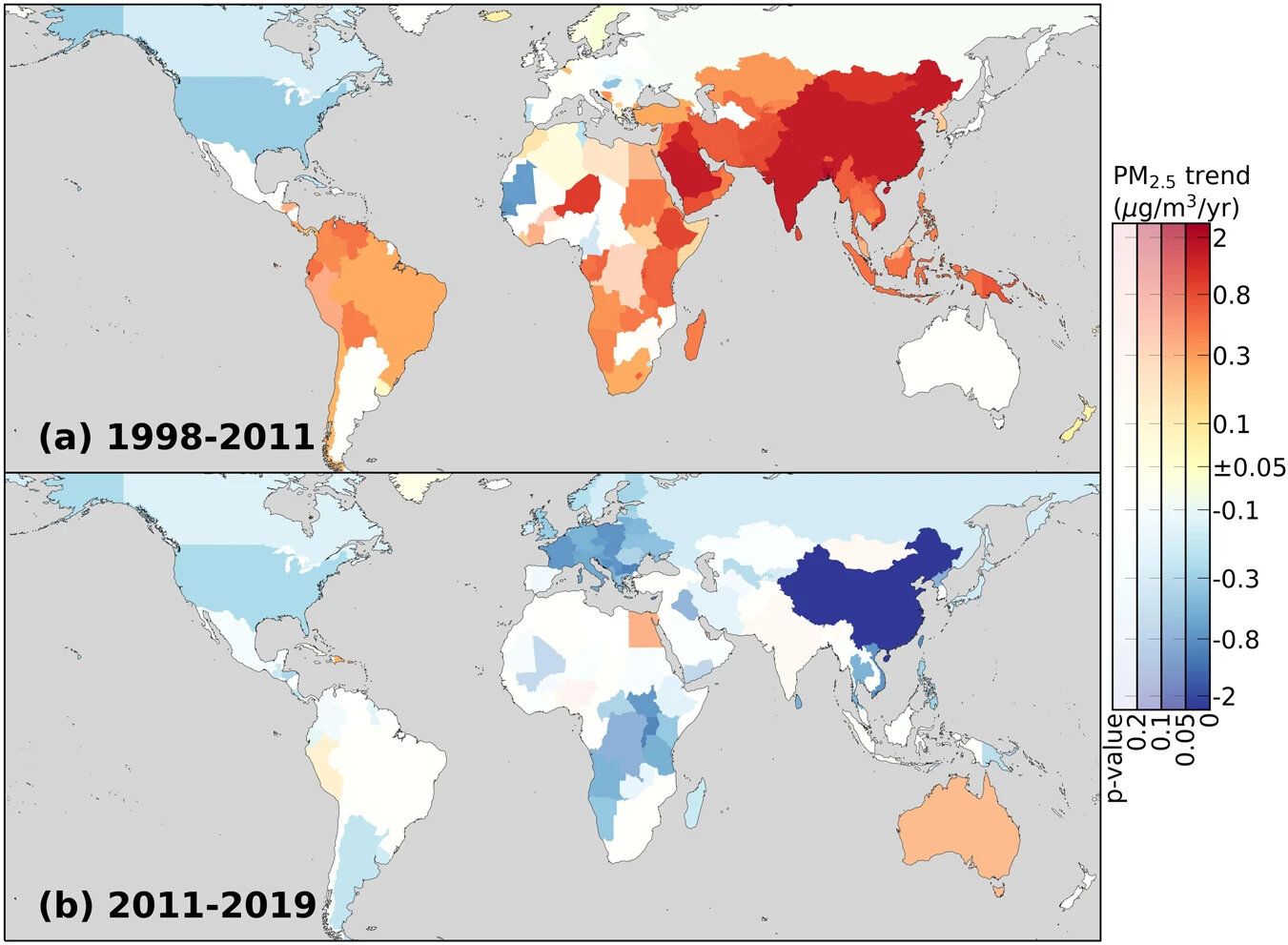
A study published in Nature Communications reveals that global exposure to fine particulate matter (PM2.5) air pollution has decreased since 2011, largely driven by reductions in China and slower growth in other regions. The study highlights the effectiveness of PM2.5 mitigation efforts, with China's rigorous air quality management contributing to a significant reduction in global mean exposure. However, there is still an urgent need for further reduction in PM2.5 exposure, as millions of premature deaths worldwide can still be attributed to it. Continued monitoring and evaluation of mitigation efforts, especially in poorly monitored but highly populated regions, are crucial for improving air quality and addressing the health impacts of PM2.5 pollution.
Reading Insights
0
1
3 min
vs 4 min read
86%
769 → 111 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Phys.org