Cascadia fault's warm liquid spewing offers earthquake hazard clues.
TL;DR Summary
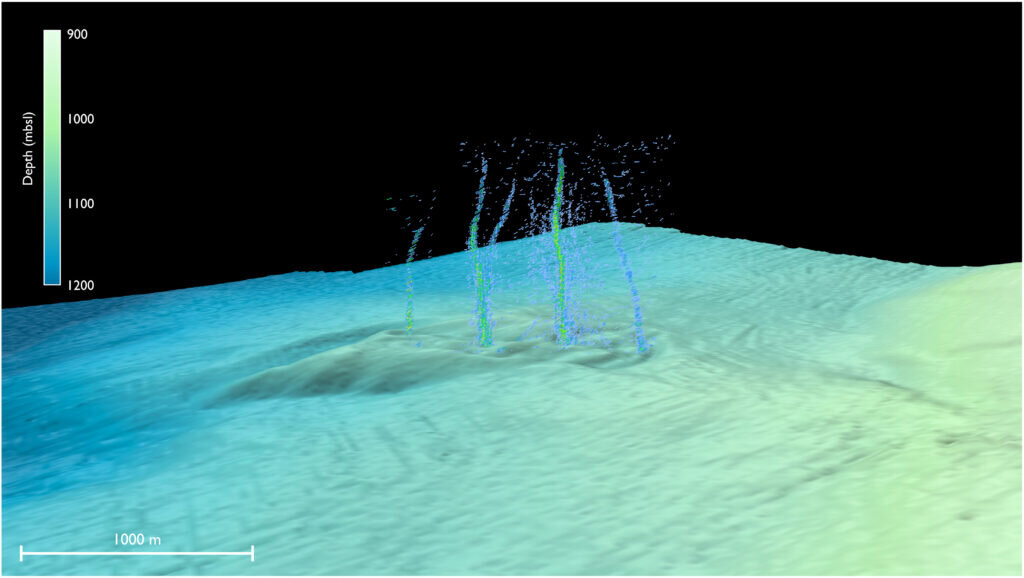
Warm, chemically distinct fluid gushing from the seafloor sediment off the coast of Oregon is believed to come directly from the Cascadia megathrust zone, regulating stress on the offshore fault. The discovery of the unique underwater spring, named Pythia's Oasis, was made by researchers from the University of Washington during a weather-related delay for a cruise aboard the RV Thomas G. Thompson. The fluid seeps are important because they lower the fluid pressure between the sediment particles and hence increase the friction between the oceanic and continental plates, which can lead to damaging earthquakes.
Topics:science#cascadia-subduction-zone#earth-science#earthquake-hazards#oceanography#plate-tectonics#seafloor
Reading Insights
Total Reads
0
Unique Readers
5
Time Saved
4 min
vs 5 min read
Condensed
89%
825 → 94 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Phys.org