The Encroaching Gulf Stream: A Warming Threat to Coastal Areas
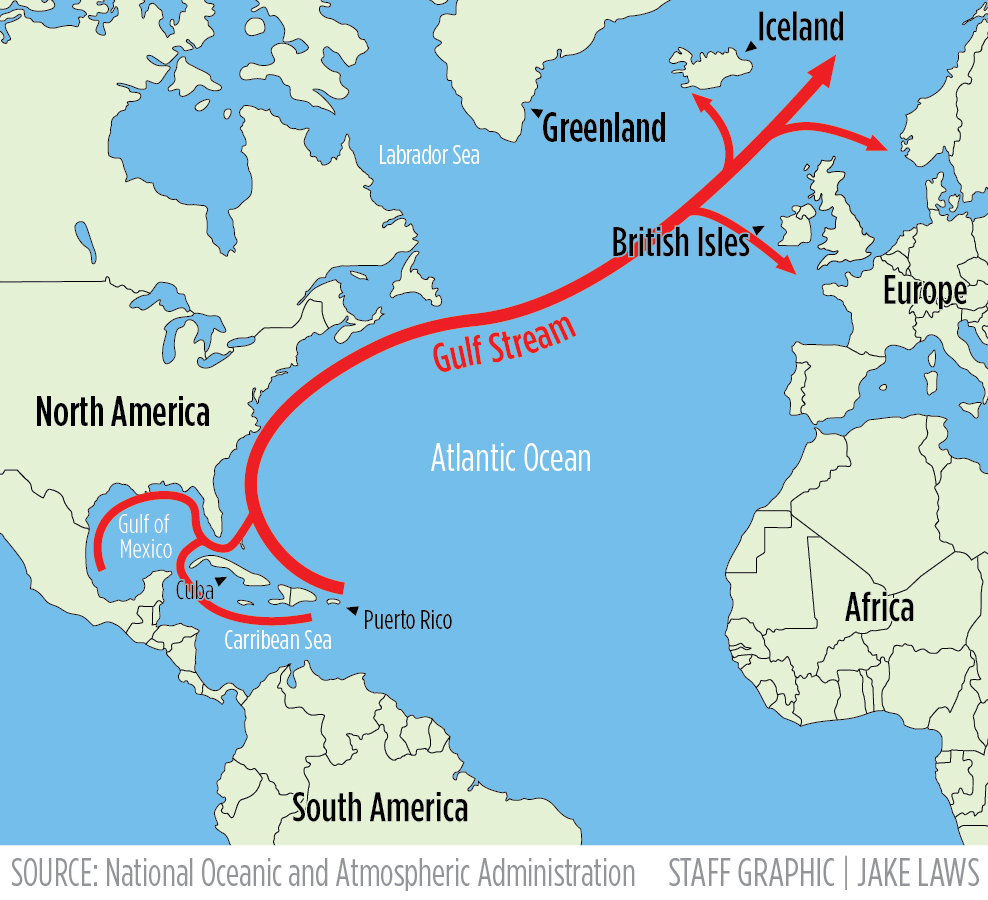
The Gulf Stream, a tropical ocean current, has warmed faster than the global oceans and moved closer to the U.S. eastern continental shelf over the past 20 years, increasing the risk of sudden impacts on coastal fisheries, according to a study by the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution. Warm-water breakaways from the Gulf Stream can temporarily increase temperatures in the Gulf of Maine, affecting marine wildlife. The balance between the Labrador Current and the Gulf Stream is shifting, with the Gulf Stream becoming warmer and wider. The warming trend in the Gulf of Maine is four times faster than the global oceans, with significant consequences for the region's ecosystems and communities.
Reading Insights
0
8
3 min
vs 5 min read
86%
805 → 110 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Press Herald