Stanford's Cancer Breakthrough: Targeting Rogue ecDNA Defies Mendel's Law
TL;DR Summary
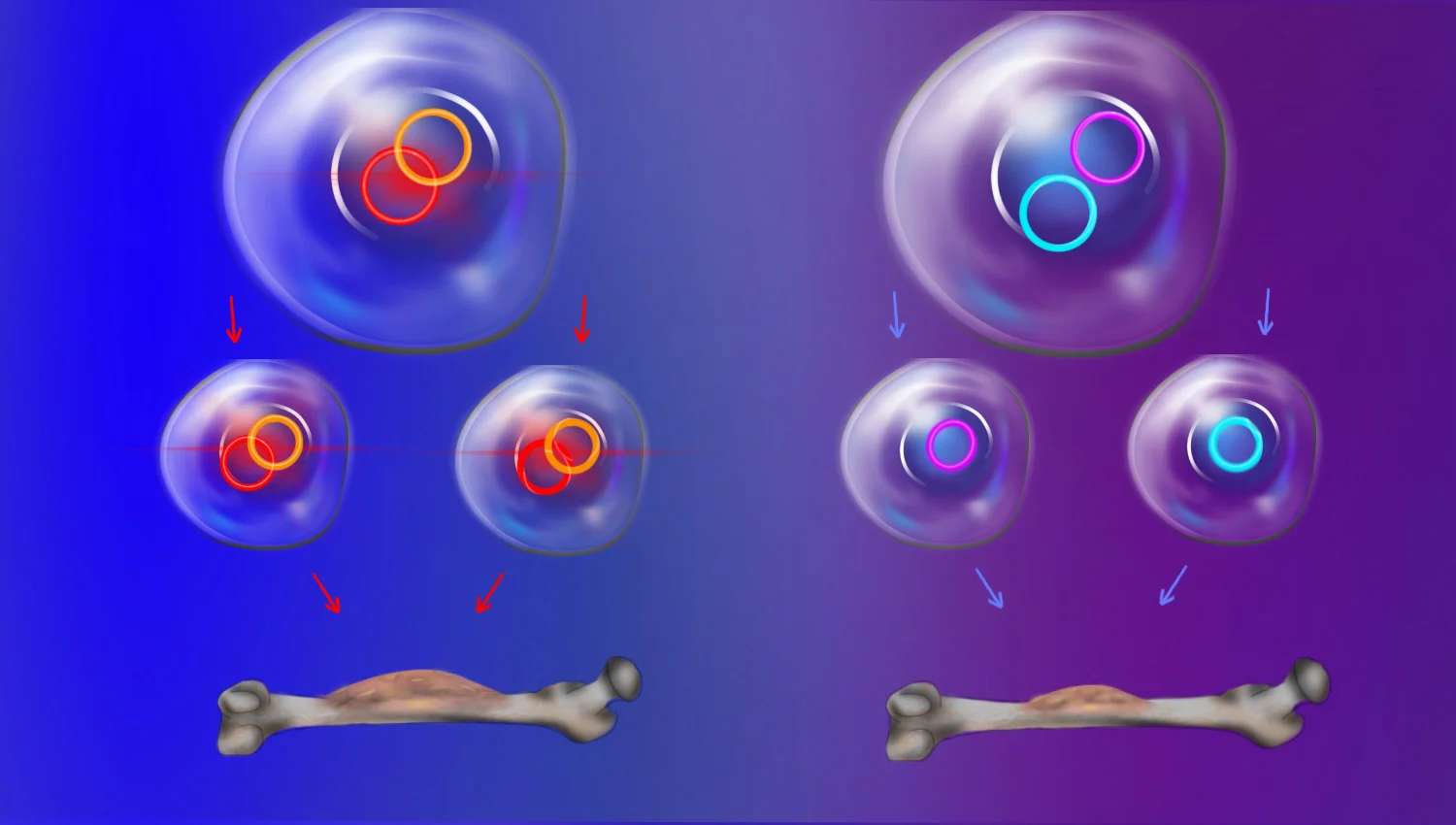
Stanford Medicine researchers have discovered that extrachromosomal DNA (ecDNA), previously considered insignificant, plays a crucial role in cancer development. Their studies reveal that ecDNA is present in 17.1% of tumors and can drive cancer growth by containing oncogenes and immune-modulating genes. This challenges Mendel's law of independent assortment, as ecDNA can be inherited together, enhancing cancer cell survival. The research also identifies a potential cancer therapy targeting ecDNA, with a CHK1 inhibitor currently in clinical trials.
- Stanford Scientists Overturn Mendel’s Law With Shocking Cancer Discovery SciTechDaily
- Breakthrough research reveals how to target malignant DNA in aggressive cancers News-Medical.Net
- How ecDNA Fuels Cancer by Breaking the Laws of Biology Howard Hughes Medical Institute
- Study raises hopes of treating aggressive cancers by zapping rogue DNA The Guardian
- Extrachromosomal DNA Spread Oncogenic Traits, Add Synthetic Lethal Targets Inside Precision Medicine
Reading Insights
Total Reads
0
Unique Readers
10
Time Saved
9 min
vs 9 min read
Condensed
96%
1,798 → 76 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on SciTechDaily