"Unveiling the Brain's Daydream Interruption Mechanism"
TL;DR Summary
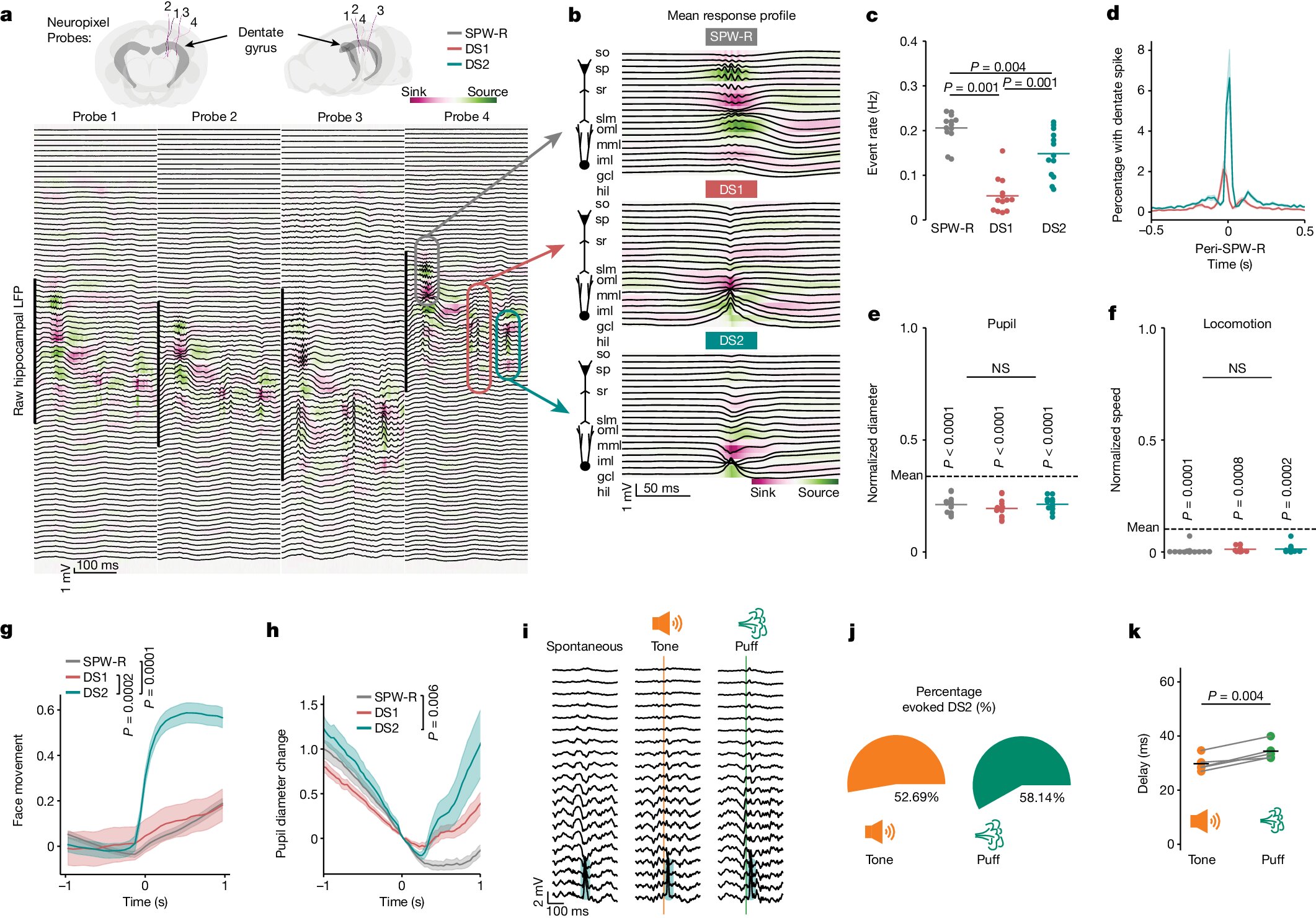
Researchers at Boston Children's Hospital have discovered that a part of the brain called the dentate gyrus plays a crucial role in snapping our attention back from daydreaming and forming memories. This neural activity, known as dentate spikes, helps us quickly process new information and orient ourselves to our environment, as well as promote associative memory. The findings could have implications for understanding neuropsychiatric disorders such as ADHD, PTSD, and epilepsy, and may lead to new treatments for these conditions.
How the brain wakes us from daydreams Medical Xpress
Reading Insights
Total Reads
0
Unique Readers
1
Time Saved
2 min
vs 3 min read
Condensed
84%
502 → 80 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Medical Xpress