"Myelination's Role in Opioid Addiction Learning"
TL;DR Summary
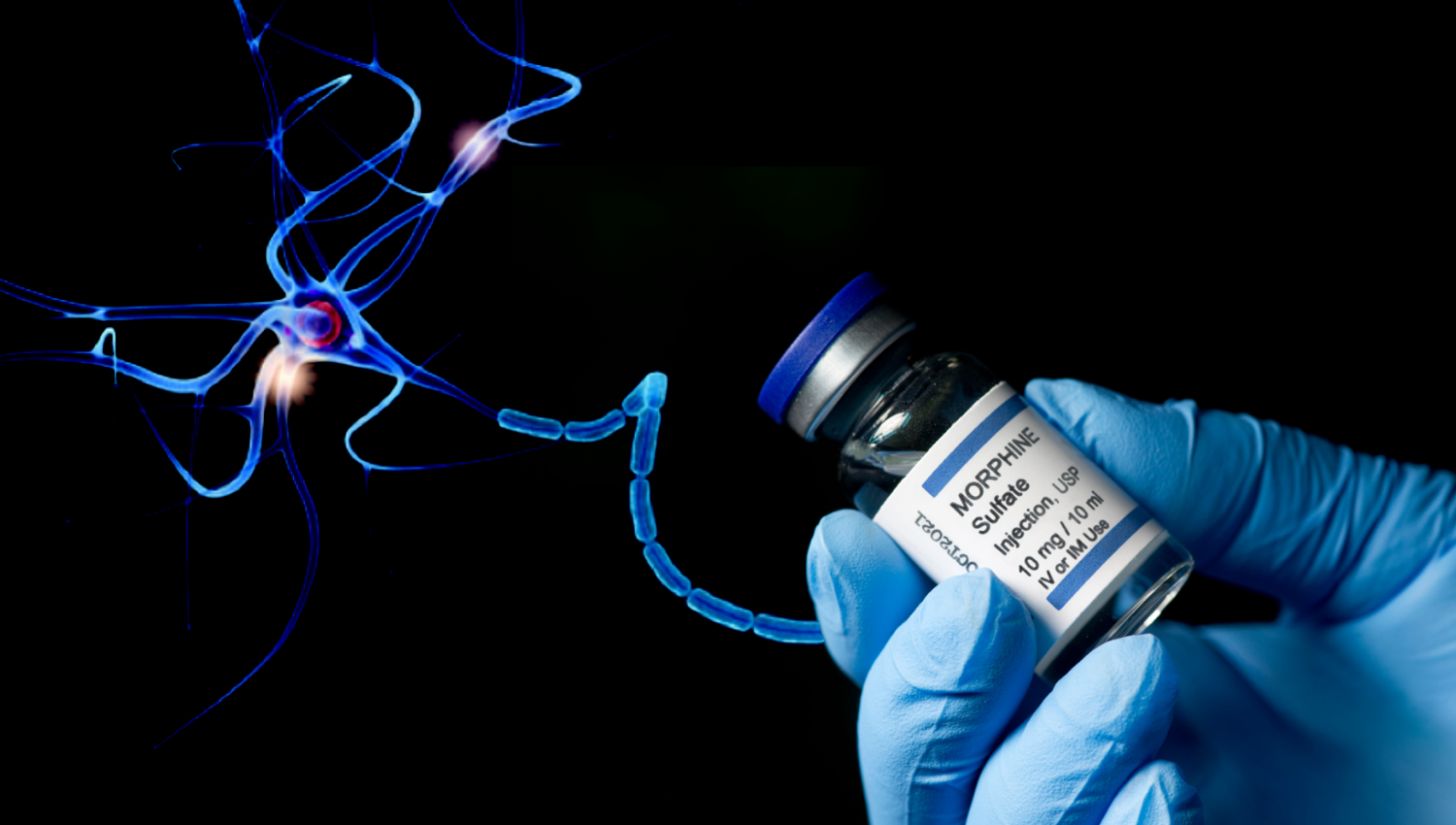
Stanford Medicine research reveals that adaptive myelination, a process crucial for learning and skill acquisition, can also promote opioid addiction by enhancing the brain's reward circuitry. In mice, a single dose of morphine triggered myelination of dopamine-producing neurons, leading to drug-seeking behavior. Blocking myelination prevented addiction, suggesting potential strategies for treating opioid dependence.
Topics:health#dopamine#health-and-science#myelination#neuroplasticity#opioid-addiction#stanford-medicine
Myelination in the brain may be key to 'learning' opioid addiction Stanford Medical Center Report
Reading Insights
Total Reads
0
Unique Readers
1
Time Saved
6 min
vs 7 min read
Condensed
96%
1,305 → 53 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Stanford Medical Center Report