D.C. Solves Child Care Crisis with Wealth Tax
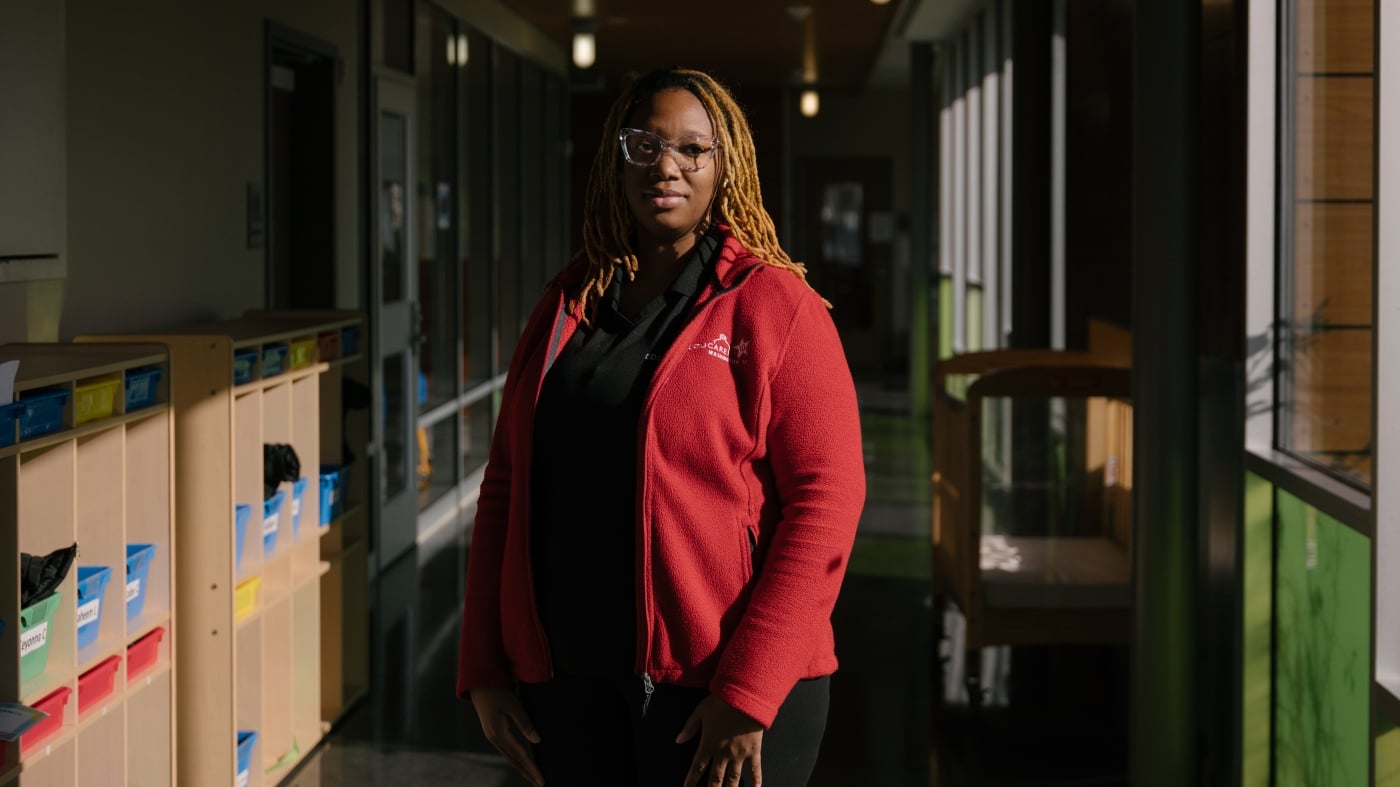
Washington, D.C. addressed its child care worker shortage by implementing a tax hike on high earners to fund the Early Childhood Educator Pay Equity Fund, significantly increasing wages for child care workers. This initiative has led to reduced turnover, improved care quality, and a 23% return on investment. However, challenges remain, such as the exclusion of administrators from wage increases and potential loss of public benefits for some workers. The program's future is uncertain due to budget concerns, despite its success.