"Uncovering the Role of Schwann Cells in Sensation"
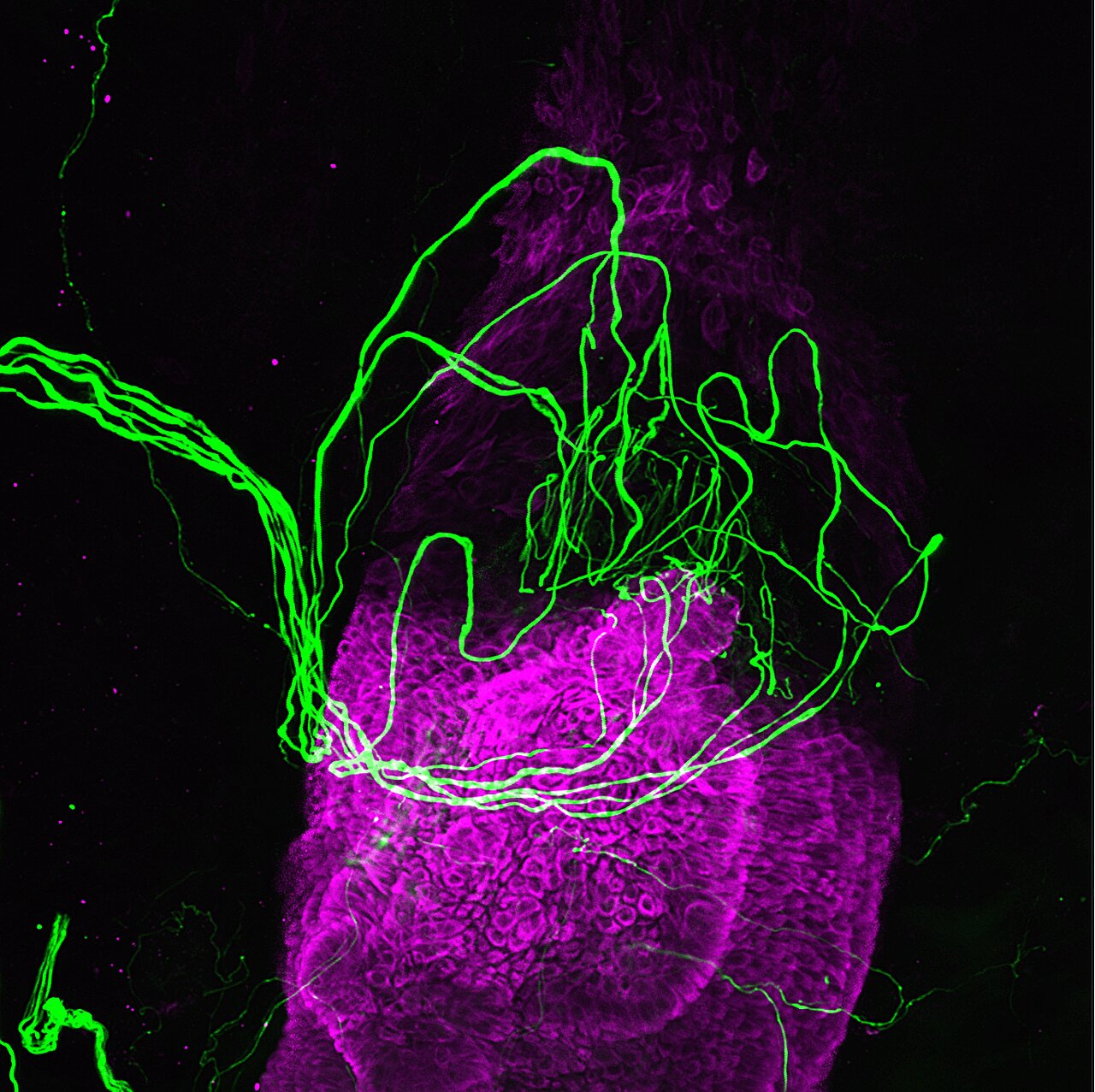
Schwann cells, traditionally known for insulating nerve fibers, have been discovered to play a crucial role in detecting sensory stimuli such as touch and pain. This groundbreaking study utilized optogenetics to manipulate these cells in mice, demonstrating their significant role in transmitting pain sensations and potential as a novel target for pain therapy. The findings challenge the existing understanding of sensory perception and offer promising new directions for treating pain and tactile impairments.