Advancements in Magnet-Wave Control and Observation with Superconductors
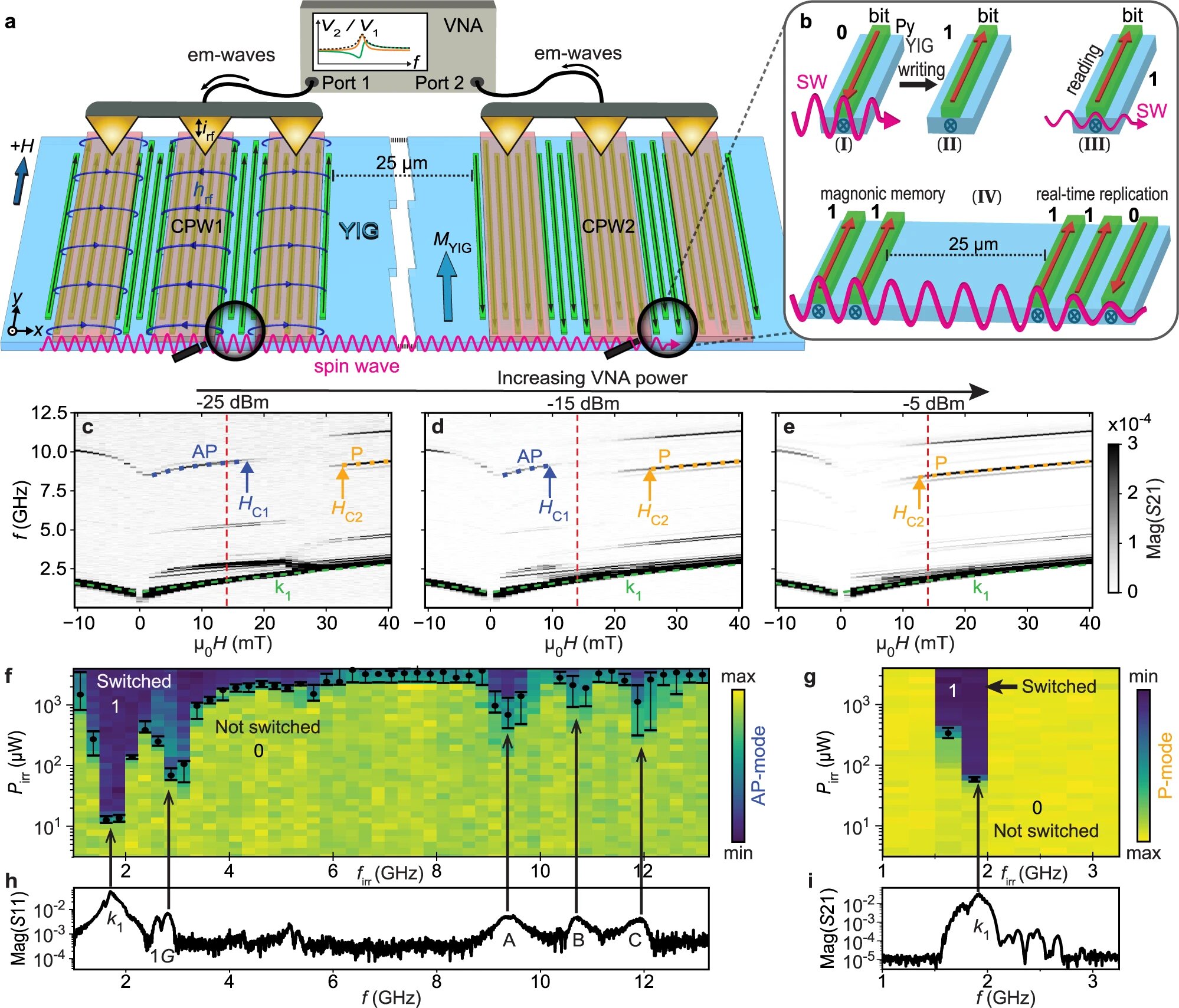
Researchers at Delft University of Technology have successfully demonstrated the control and manipulation of spin waves on a chip using superconductors, providing new insights into the interaction between magnets and superconductors. Spin waves, which are waves in magnetic materials, have the potential to be used as an energy-efficient alternative to electronics. By using a superconducting electrode, the researchers were able to reflect and control the spin waves, allowing for precise manipulation. This breakthrough opens the door for the development of energy-efficient spin-wave circuits and devices, such as frequency filters and resonators, as well as applications in quantum computing.