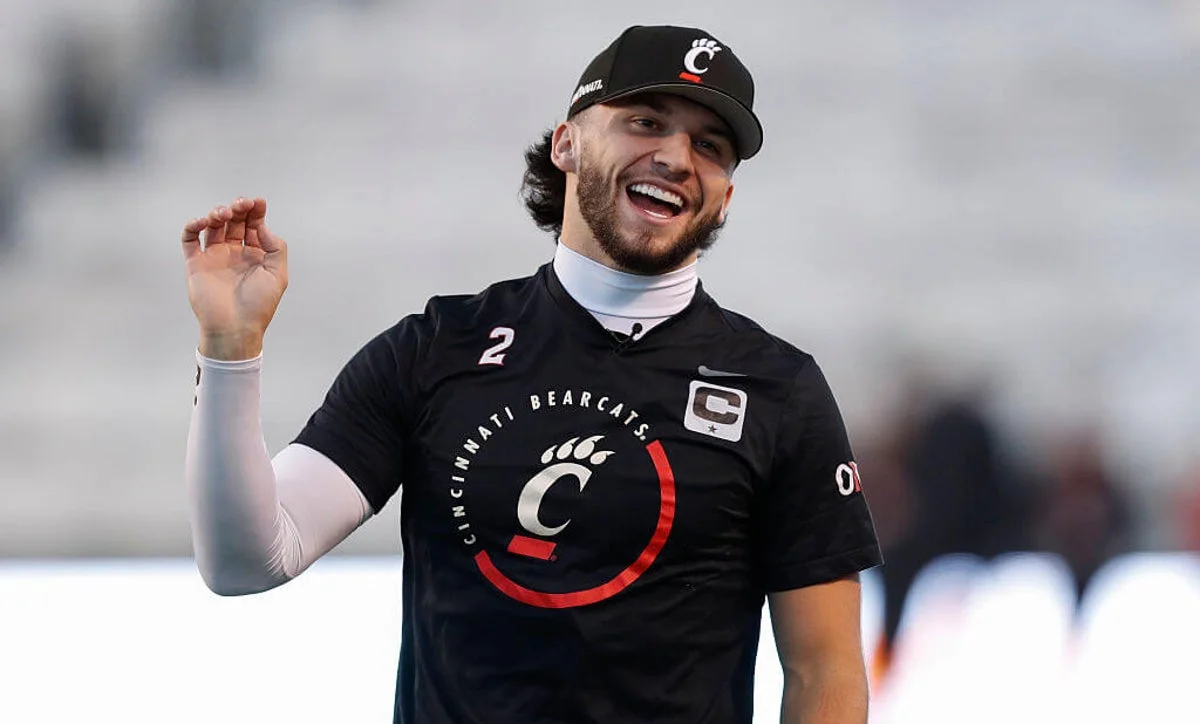
Bearcats seek $1M NIL buyout from ex-QB after Texas Tech transfer
UC filed a breach-of-contract suit seeking $1 million in liquidated damages from Brendan Sorsby for transferring to Texas Tech before completing a two-season NIL/revenue-sharing agreement; Cincinnati says the buyout clause applies, Sorsby’s camp disputes the claim, and Tech declined comment as the case underscores ongoing questions about enforcing rev-share contracts in college sports.