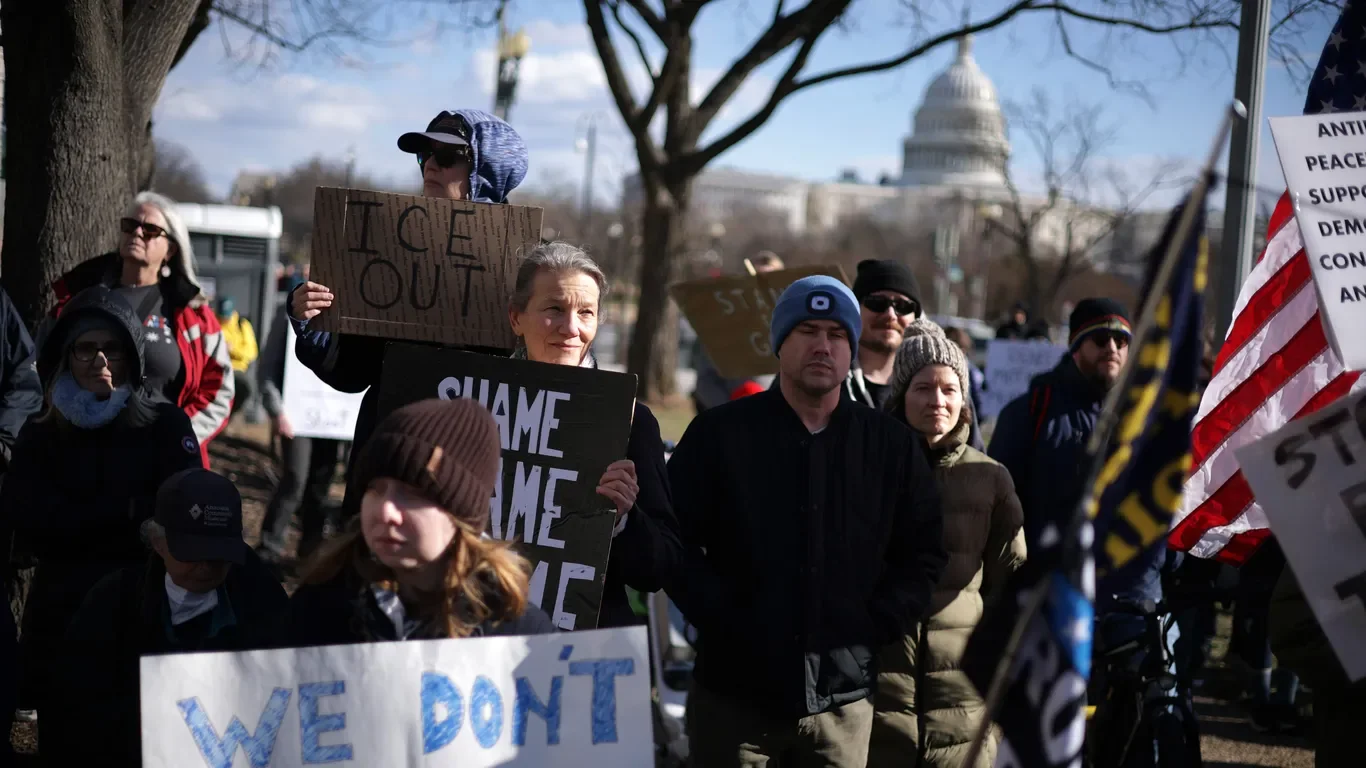
Democratic Rift Widens Over ICE Response After Minneapolis Shooting
House Democrats are divided over how to respond to sharp anti-ICE sentiment following the Minneapolis shooting of Renee Good, with some lawmakers pushing impeaching DHS Secretary Kristi Noem and others advocating tighter ICE oversight through funding changes and a QR-code on agents’ uniforms; leadership is trying to keep caucus focus on economy, affordability and health care, and while some push for funding cuts or policy changes, several centrists say defunding ICE is unlikely.














