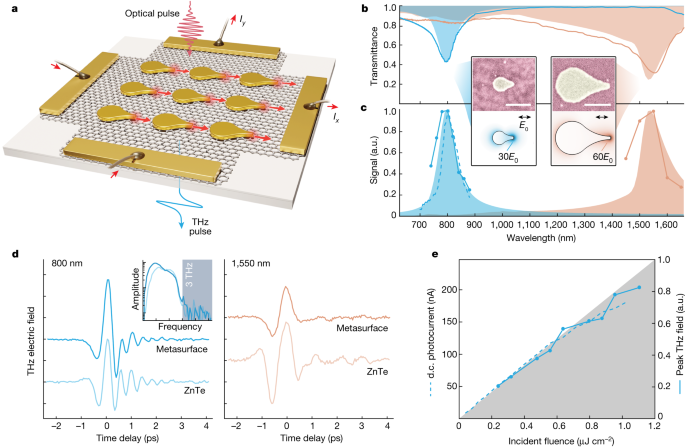
"Nanoscale Vectorial Currents Propelled by Light"
Researchers have developed plasmonic metasurfaces that can control vectorial currents at nanoscale spatial scales and femtosecond timescales. These metasurfaces, consisting of gold nanoantennas on graphene, exhibit strong, light-driven directional responses, with implications for optically controlled and globally varying vectorial photocurrents. The metasurfaces can serve as efficient sources of ultrafast terahertz radiation, including broadband THz vector beams, and can be actively manipulated by incident optical fields or electrostatic gating. The dynamics of the charge flow are studied using electromagnetic, thermodynamic, and hydrodynamic modeling, revealing the potential for spatially varying vectorial current distributions and direct generation of broadband vector beams in the THz frequency range.