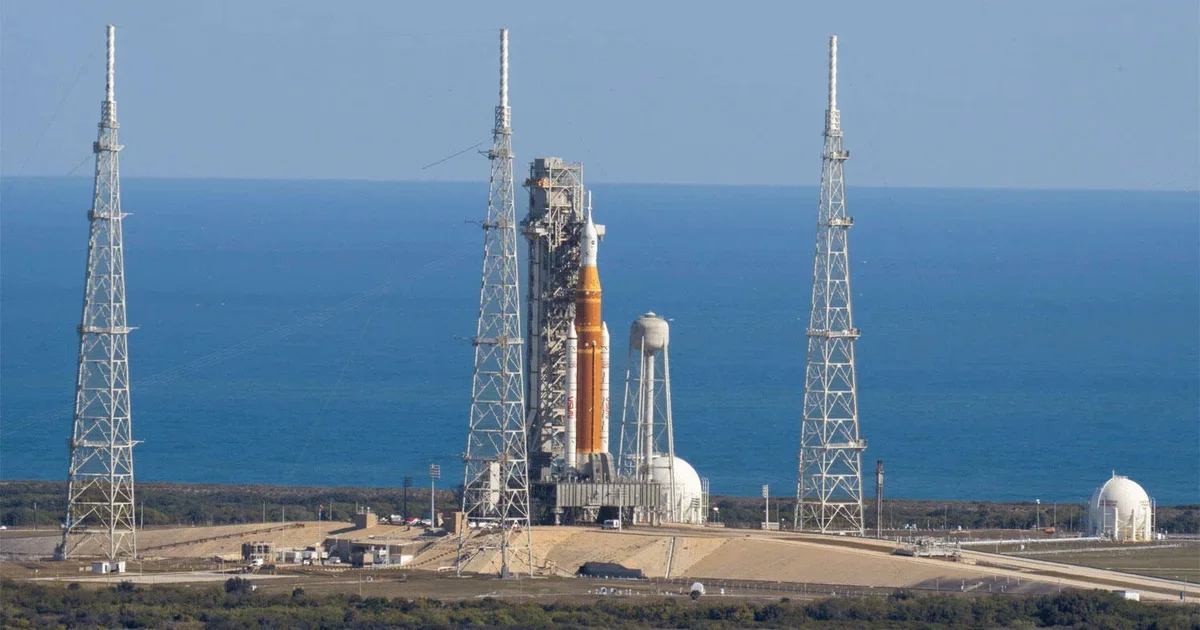
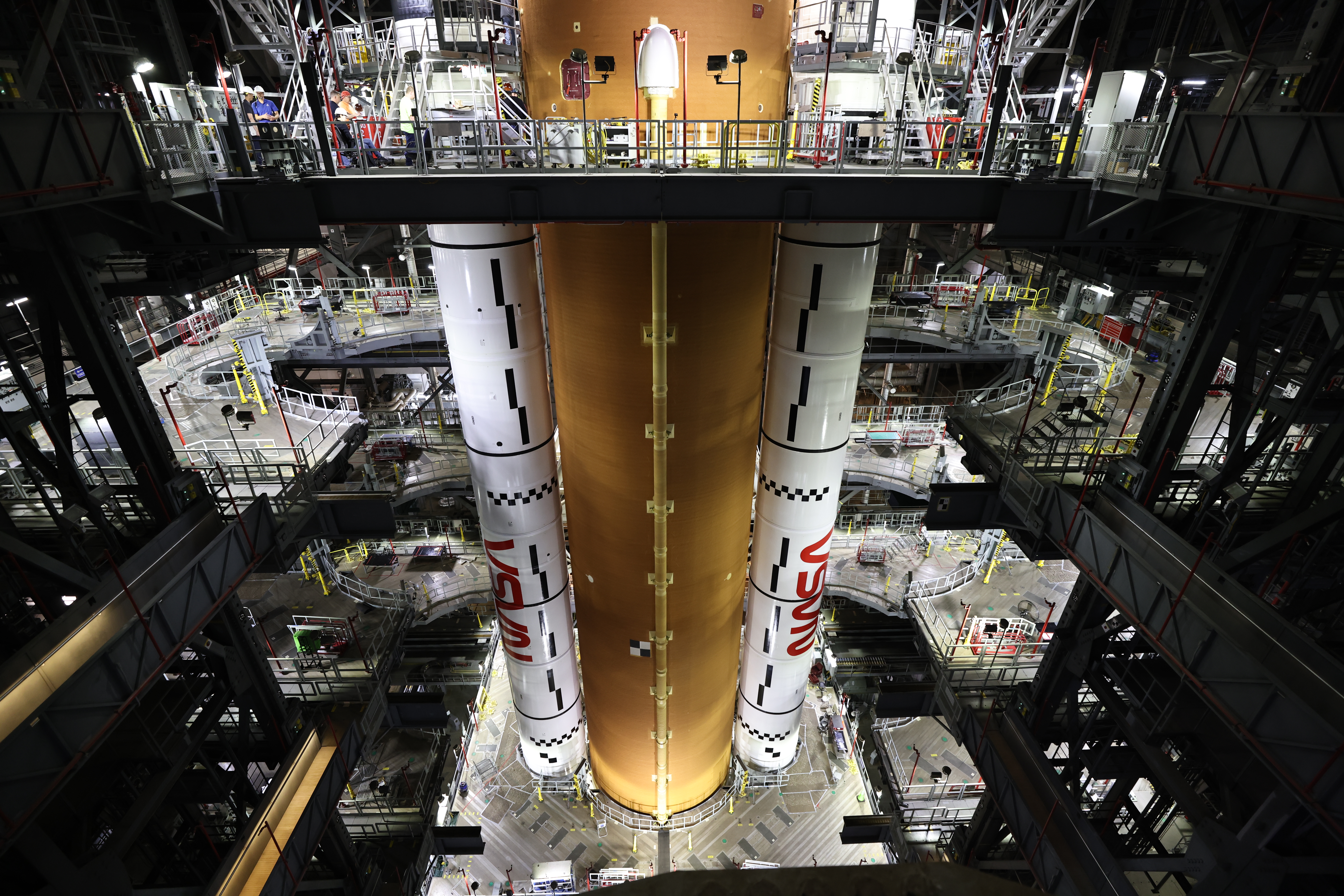
NASA to Roll Moon Rocket Back to Hangar for Repairs, Risking Artemis II's April Window
NASA plans a slow rollback of its Artemis moon rocket to Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building to diagnose a helium-system issue after hydrogen-leak fixes, a move that could preserve an April launch window for Artemis II if repairs go well and data supports it; the four astronauts are in Houston awaiting the decision.