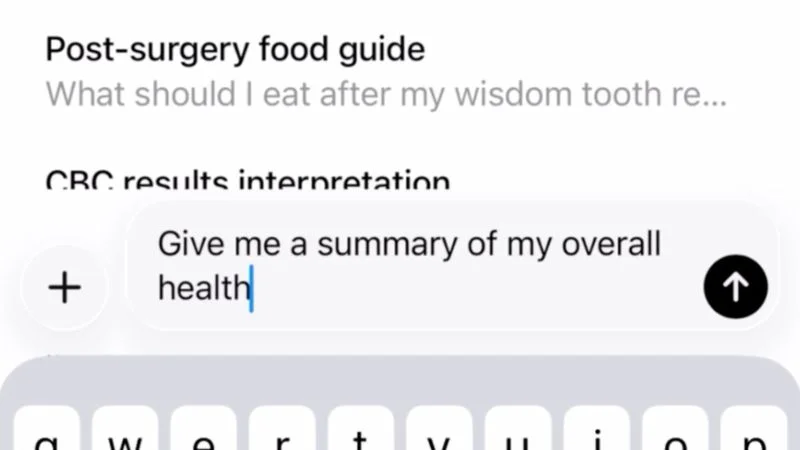
Are AI Health Chatbots Ready for Medical Advice?
AI health chatbots like OpenAI’s ChatGPT Health and Anthropic’s Claude are marketed to analyze medical records and wellness data to answer health questions, but experts caution they’re not a substitute for professional care. They can summarize test results, identify trends, and help prepare for a doctor’s visit, yet privacy protections differ from HIPAA and health data uploaded to these models isn’t guaranteed to be protected. Independent testing shows mixed results: the tools can be personalized and useful, but they can hallucinate or misinterpret user inputs. Use them with healthy skepticism, consider cross-checking with multiple AI tools or a clinician, and seek immediate medical help for emergencies or major decisions.