"Resuming Embryo Transfers: Alabama's IVF Legal Questions"
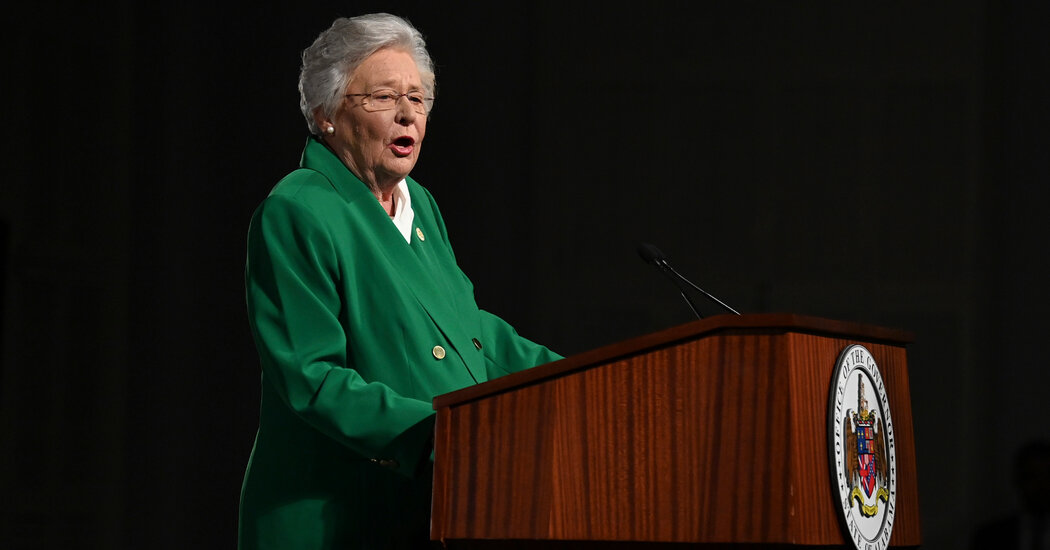
At least one Alabama fertility clinic has resumed embryo transfers following the signing of a law by Gov. Kay Ivey that provides legal protection for in vitro fertilization procedures. The law was a response to a State Supreme Court ruling that considered frozen embryos as children, causing several clinics to temporarily halt IVF treatments. While the law offers immediate relief, more legal clarity is needed to ensure the long-term continuation of IVF in the state, as the question of whether an embryo should be considered a person remains unresolved.