"Palomar Observatory Discovers Rare Two-Faced Star, Unveiling New Celestial Insights"
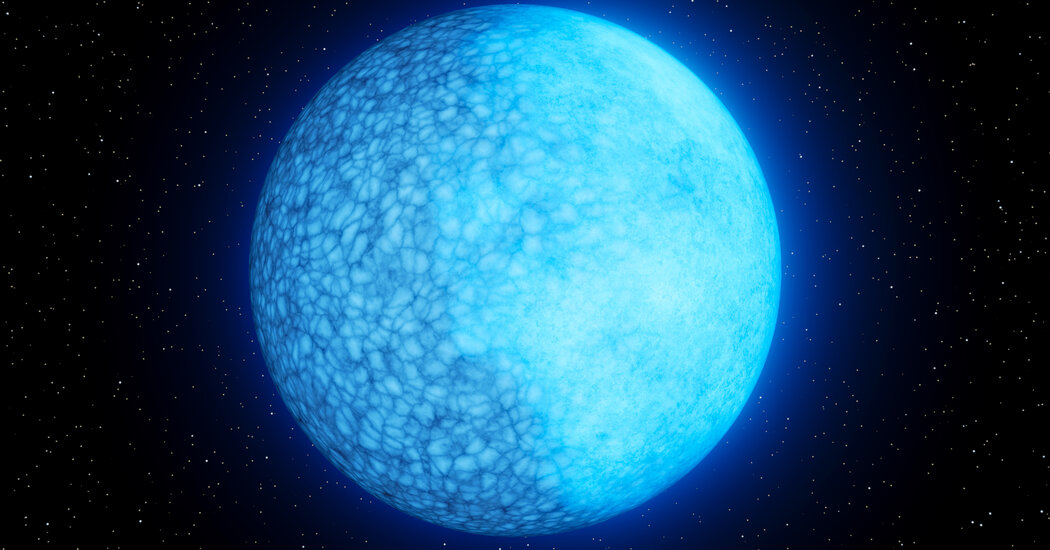
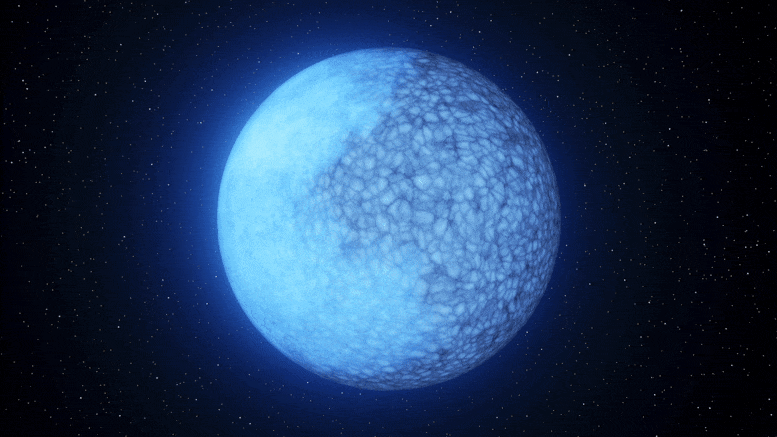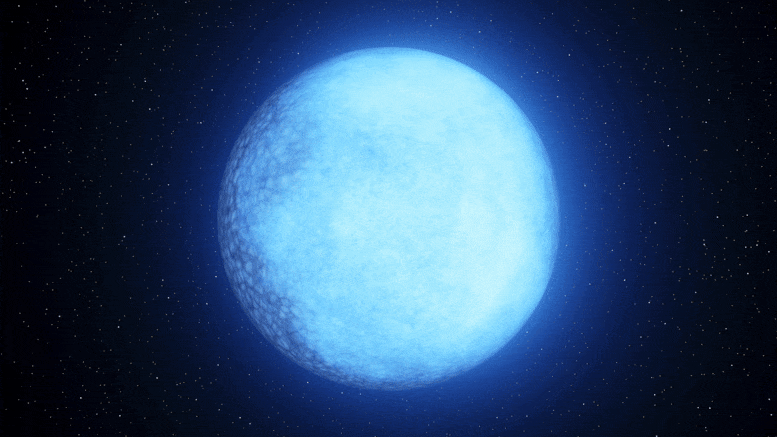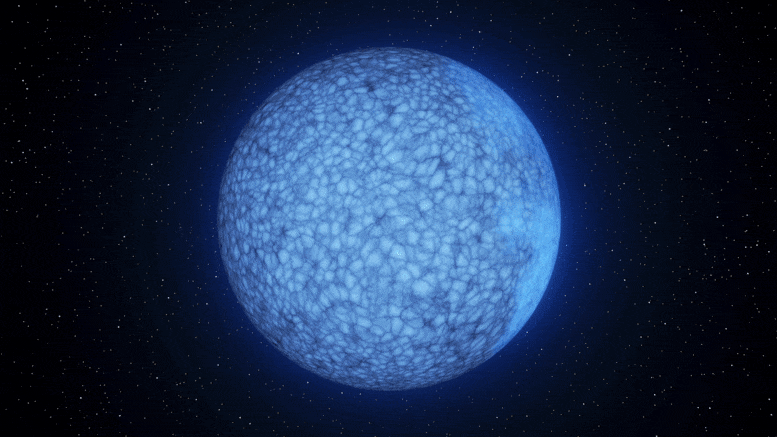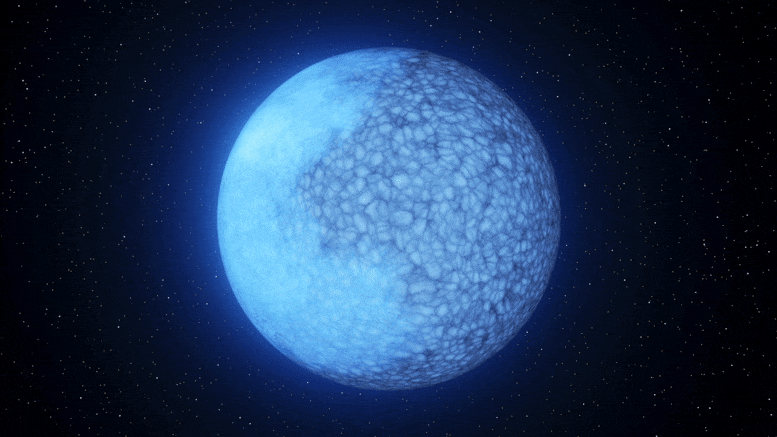
Astronomers at Palomar Observatory have discovered a rare white dwarf star named Janus that appears to have two distinct faces on its surface, one composed of hydrogen and the other of helium. This unique finding could provide insights into the evolution of white dwarfs and confirm a long-standing theory about the transition of a star's core as it burns out. The star's composition suggests a rare phase of evolution, and researchers believe that a magnetic field on Janus' surface may be responsible for the separation of hydrogen and helium. Further study of similar white dwarfs is planned to unravel the mystery.