"Revolutionizing Sickle Cell Treatments: An Opinion"
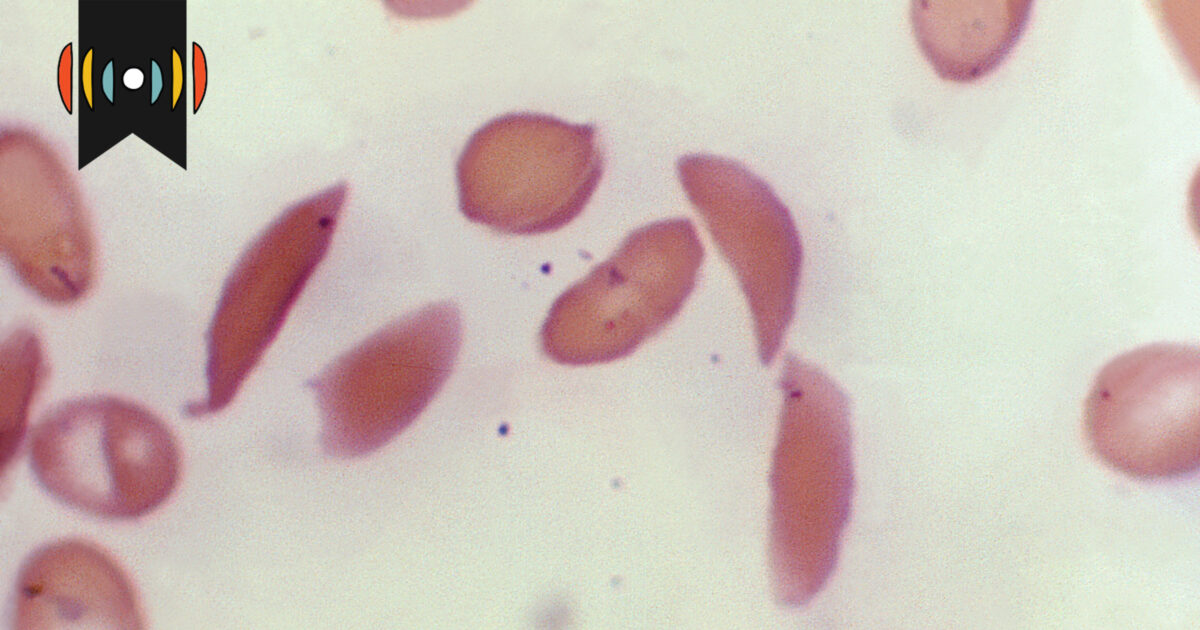
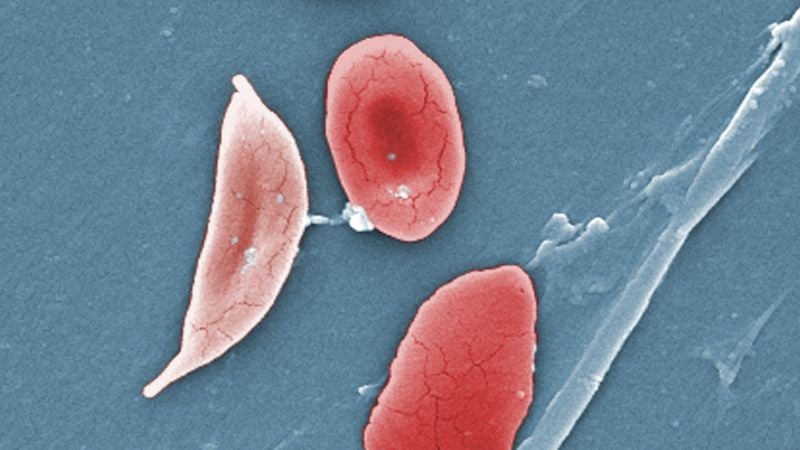
The FDA has approved two groundbreaking cell-based gene therapies, Casgevy and Lyfgenia, for treating sickle cell disease (SCD), with Casgevy being the first FDA-cleared clinical use of CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing for any condition. SCD, which disproportionately affects those with African ancestry, has long been underfunded in research and treatment. While these therapies offer hope, concerns about their high costs and accessibility remain, especially for those not enrolled in Medicaid. The ethical use of CRISPR in these therapies differs from more controversial applications, and the focus should now be on making these treatments more affordable and accessible to patients worldwide.