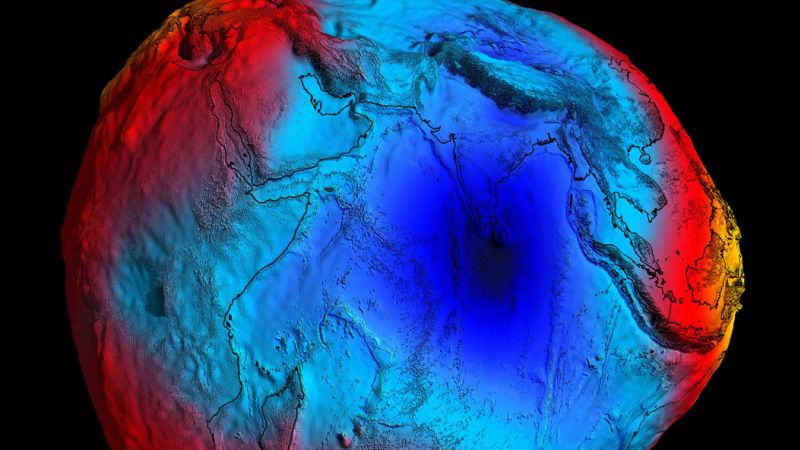
"Exploring Global Gravity: Unveiling the Most Significant Variations"
Gravity is not uniform across the Earth due to variations in mass caused by Earth's inner structure and topography. Scientists use advanced instruments and satellite data to measure these small abnormalities. The strongest gravitational forces are found in the eastern Pacific Ocean near Australia and Indonesia, resulting from plate tectonic movements. Gravity anomalies are also observed in regions such as the North American ice sheet depression and an unusual gravity hole in the Indian Ocean. Additionally, human activities, including melting polar ice caps and changes in water reservoirs, are affecting gravity. Understanding these variations is crucial for tracking climate change and water supplies.