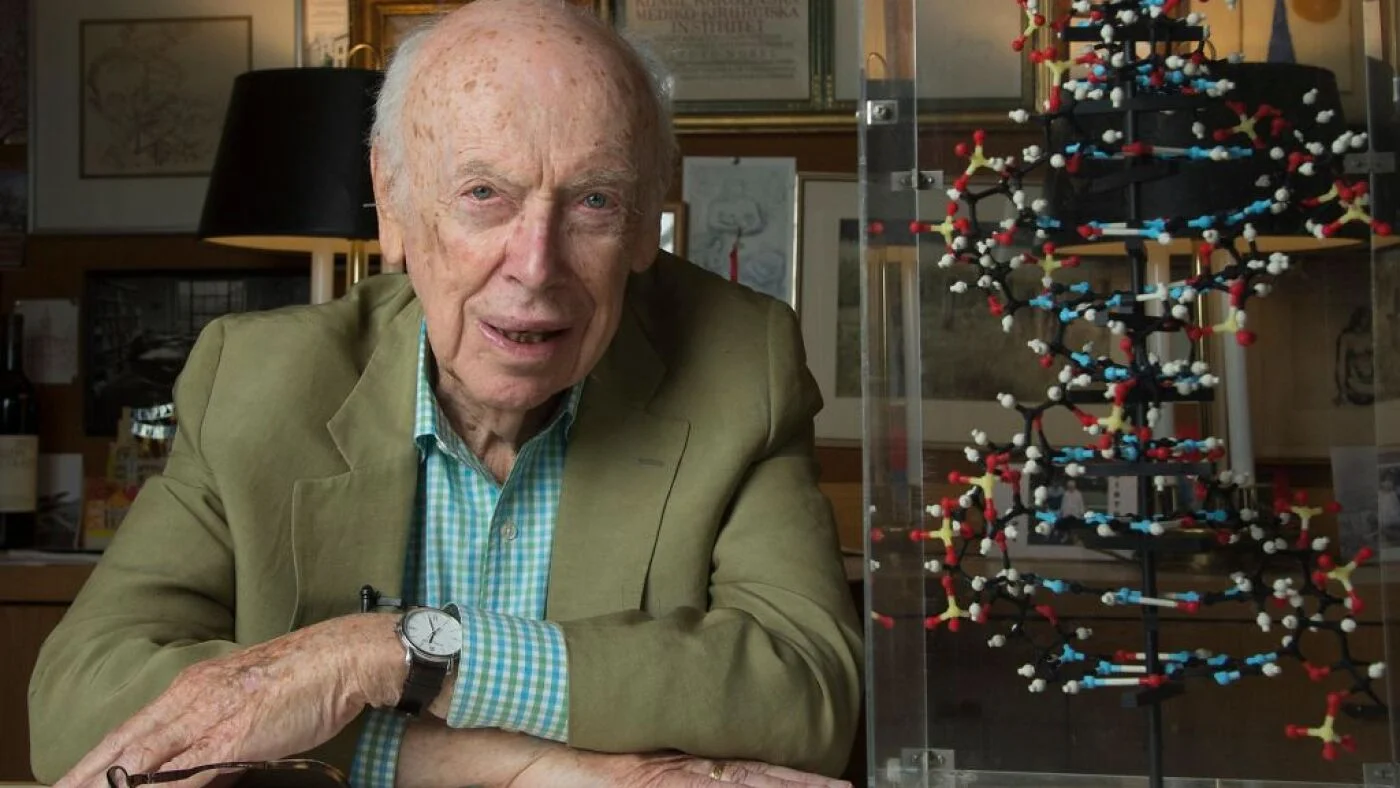
James Watson, DNA Double Helix Co-Discoverer, Dies at 97
James Watson, the co-discoverer of the DNA double helix, died at 97. His groundbreaking work transformed biology, but his later years were marred by controversial and unfounded remarks on race and gender, leading to his fall from grace and the revocation of his honors.