Antarctica's Ozone Hole Expands, Surpassing Brazil's Size
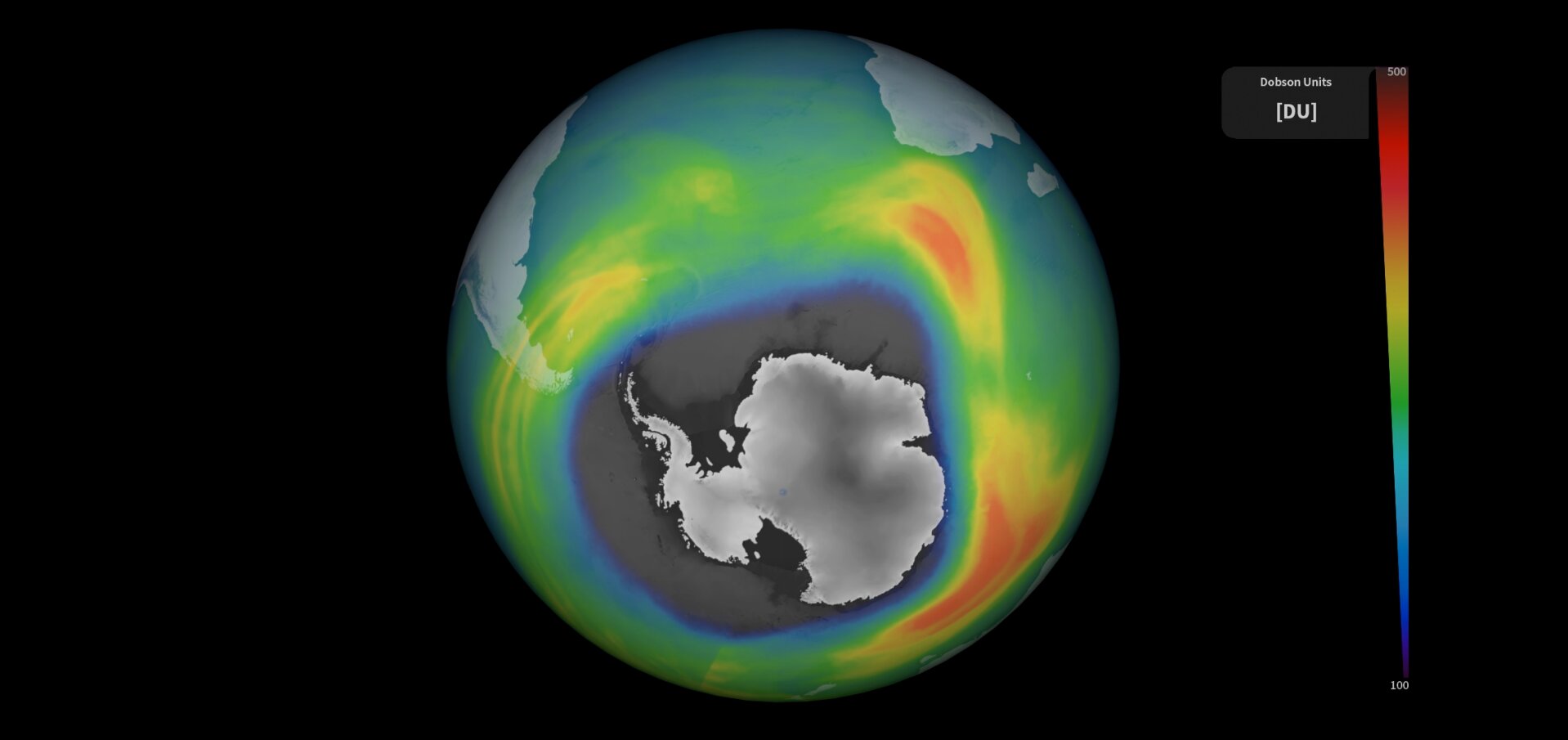
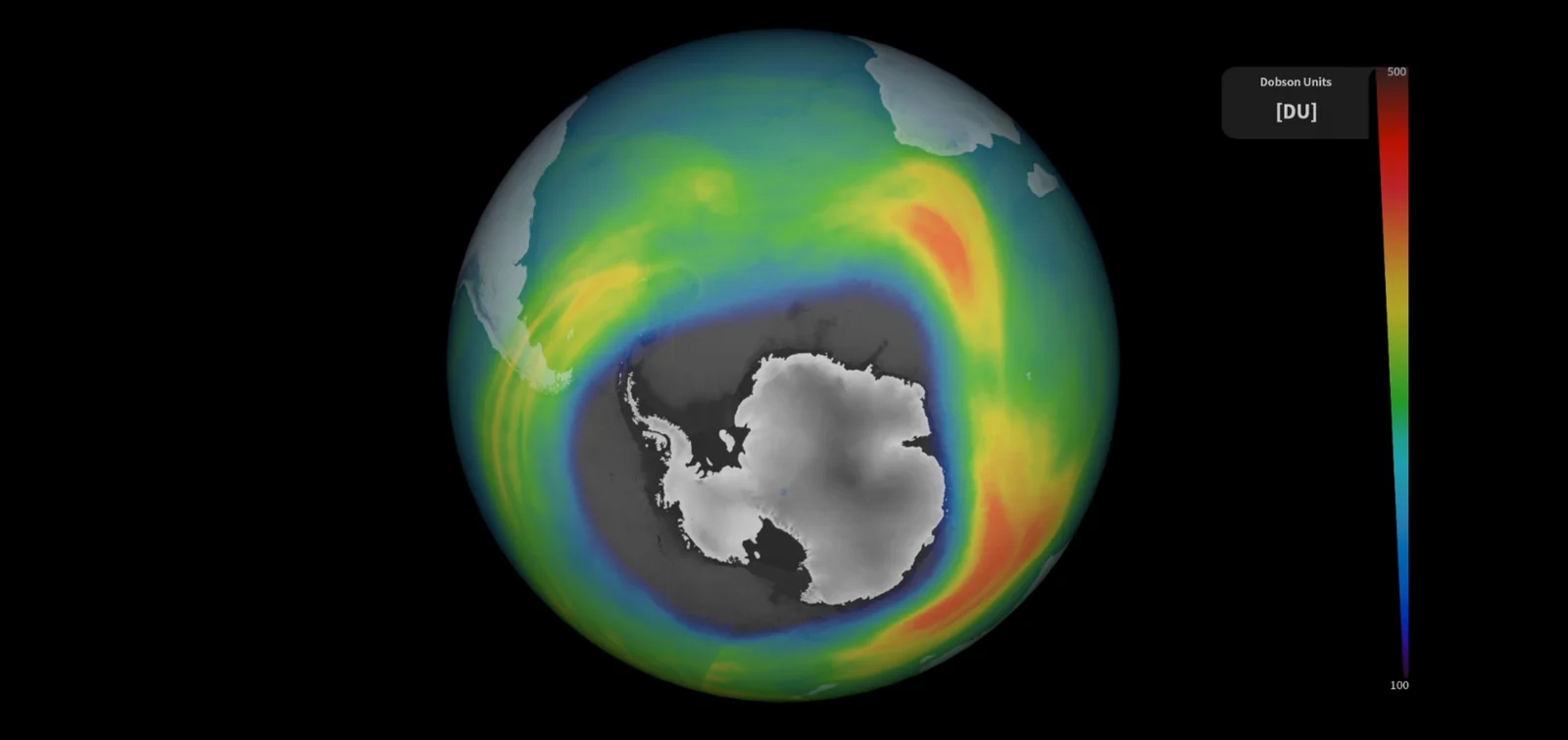
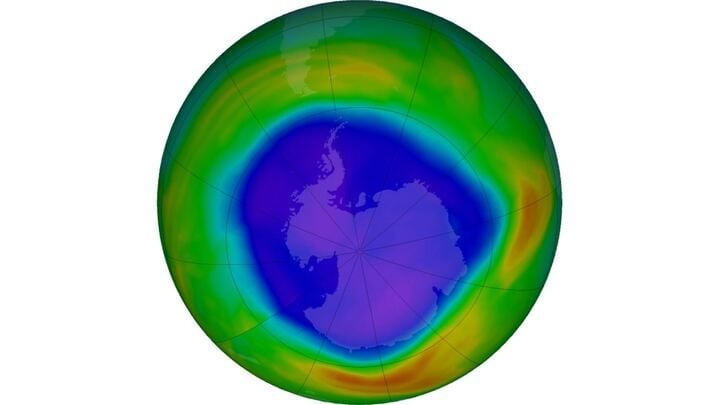
The ozone hole above Antarctica has grown to approximately 10 million square miles, making it one of the largest seasonal holes ever observed. The hole still experiences seasonal growth and shrinkage, but overall it is decreasing in size due to the Montreal Protocol and the decrease of ozone-depleting substances. The early start and rapid growth of the ozone hole this year may be attributed to the Hunga Tonga volcanic eruption in January 2022, which introduced large amounts of water vapor into the air. Scientists predict that the global ozone layer will return to its normal state by around 2050.