The Alarming Rise of Antibiotic Resistance in Children's Infections
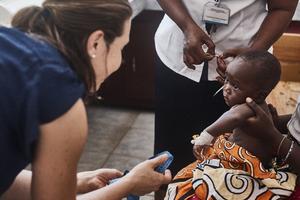
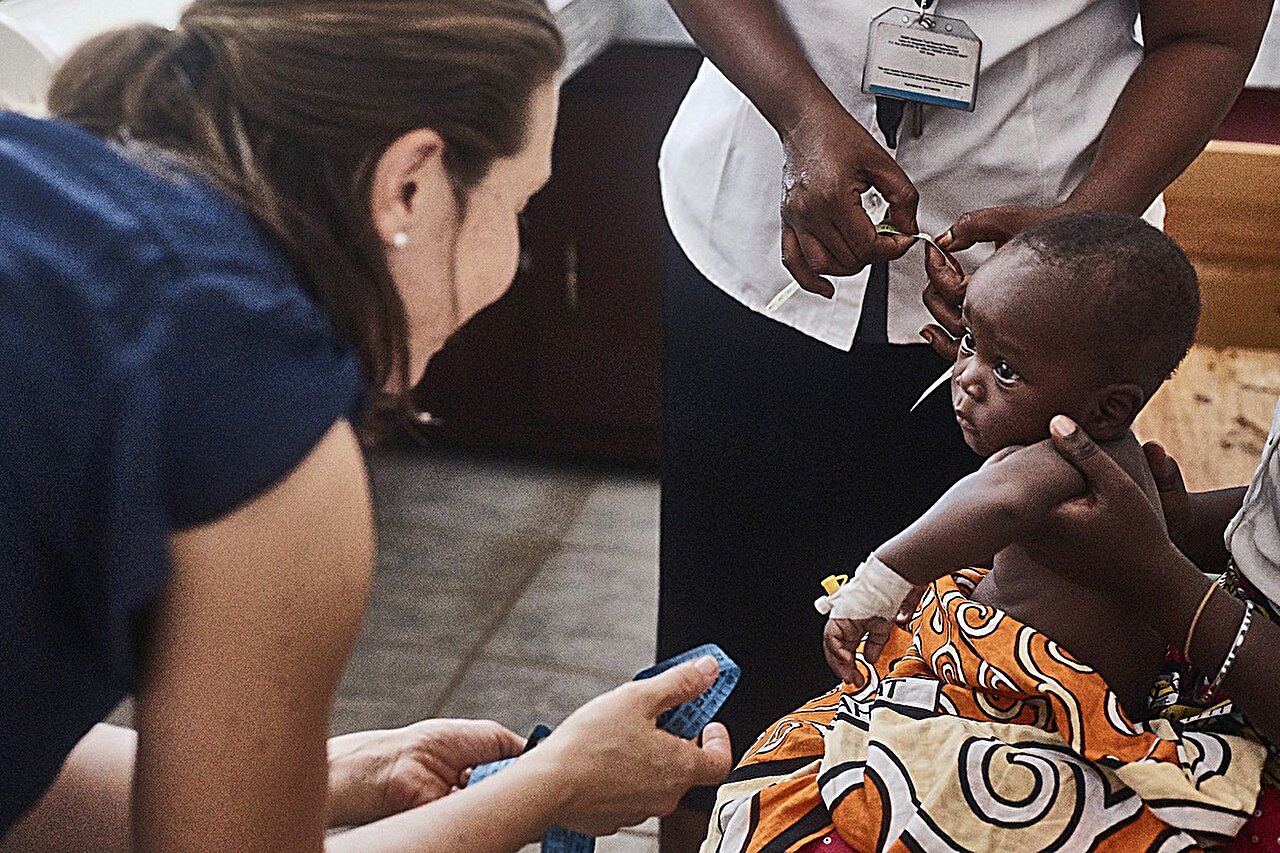
Antibiotics commonly used to treat childhood infections such as pneumonia, sepsis, and meningitis are becoming less effective, with some antibiotics now less than 50% effective, according to a study published in The Lancet Regional Health—Southeast Asia. The regions most affected by reduced efficacy are Southeast Asia and the Pacific, including Indonesia and the Philippines. Antibiotic resistance is a global threat recognized by organizations such as the World Health Organization, and it is particularly dangerous for children as new antibiotics are less likely to be developed and made available for them. The study highlights the need for prioritizing the development of new antibiotic treatments for children and newborns.