Unraveling Complexity: The Origins of Life's Building Blocks
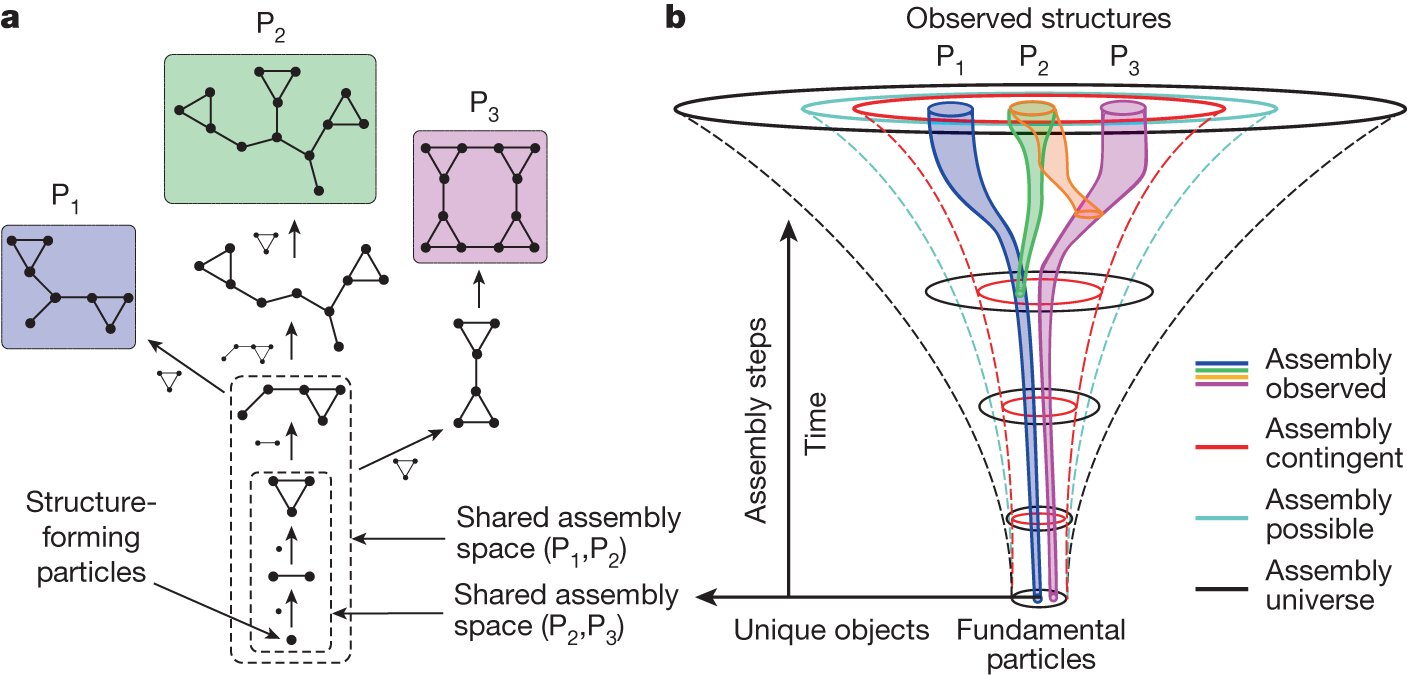
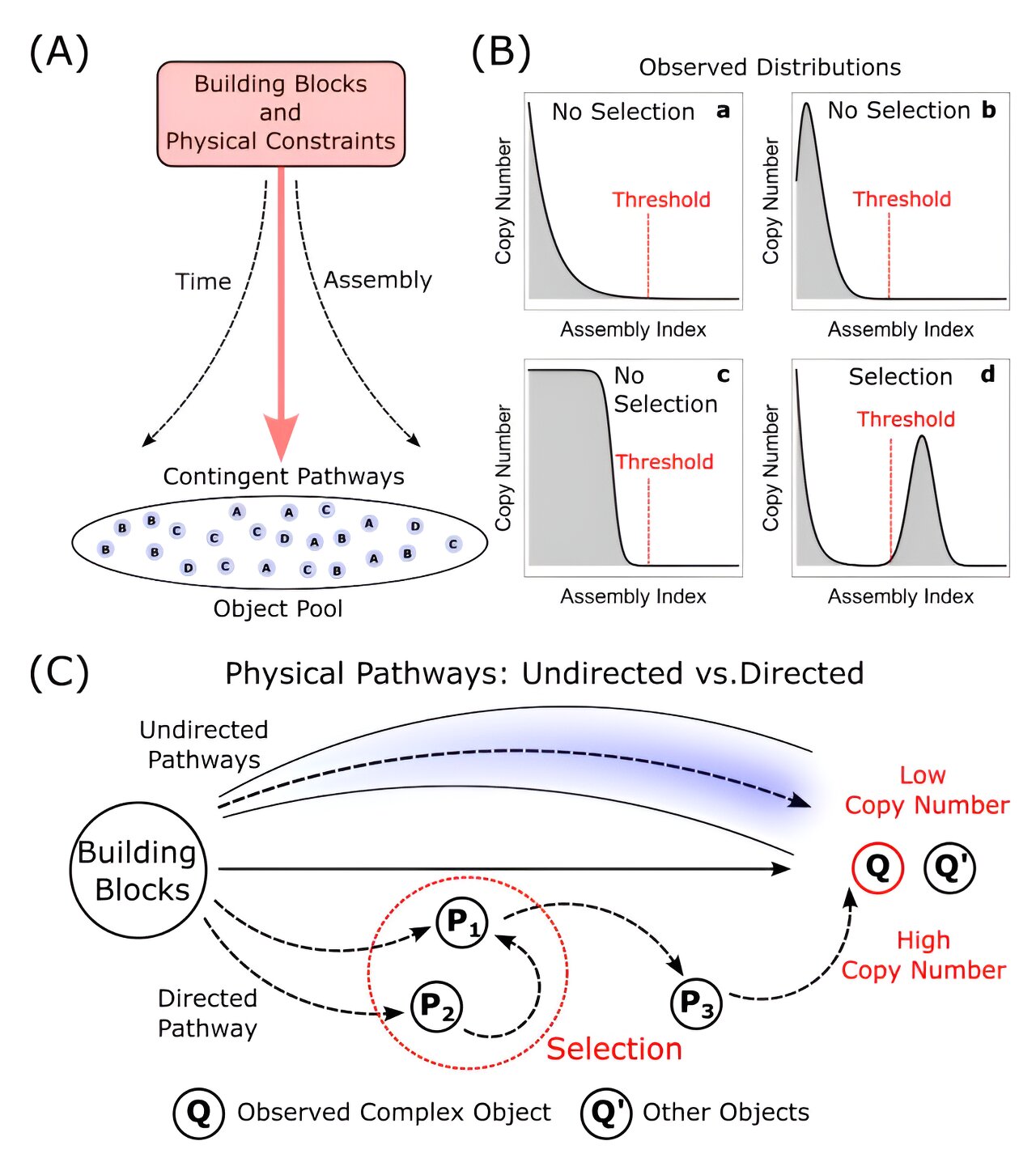
The article discusses theoretical physicist Sara Imari Walker's work on Assembly Theory, a framework exploring the rise of complexity in lifeless systems and the fundamental differences between living and non-living matter. Walker's theory emphasizes the role of information and complexity in understanding life's unique properties, focusing on how complex structures emerge and persist. The conversation highlights the importance of measuring complexity and information in physical terms, and the potential of Assembly Theory to offer new insights into life's evolution and existence in the universe.