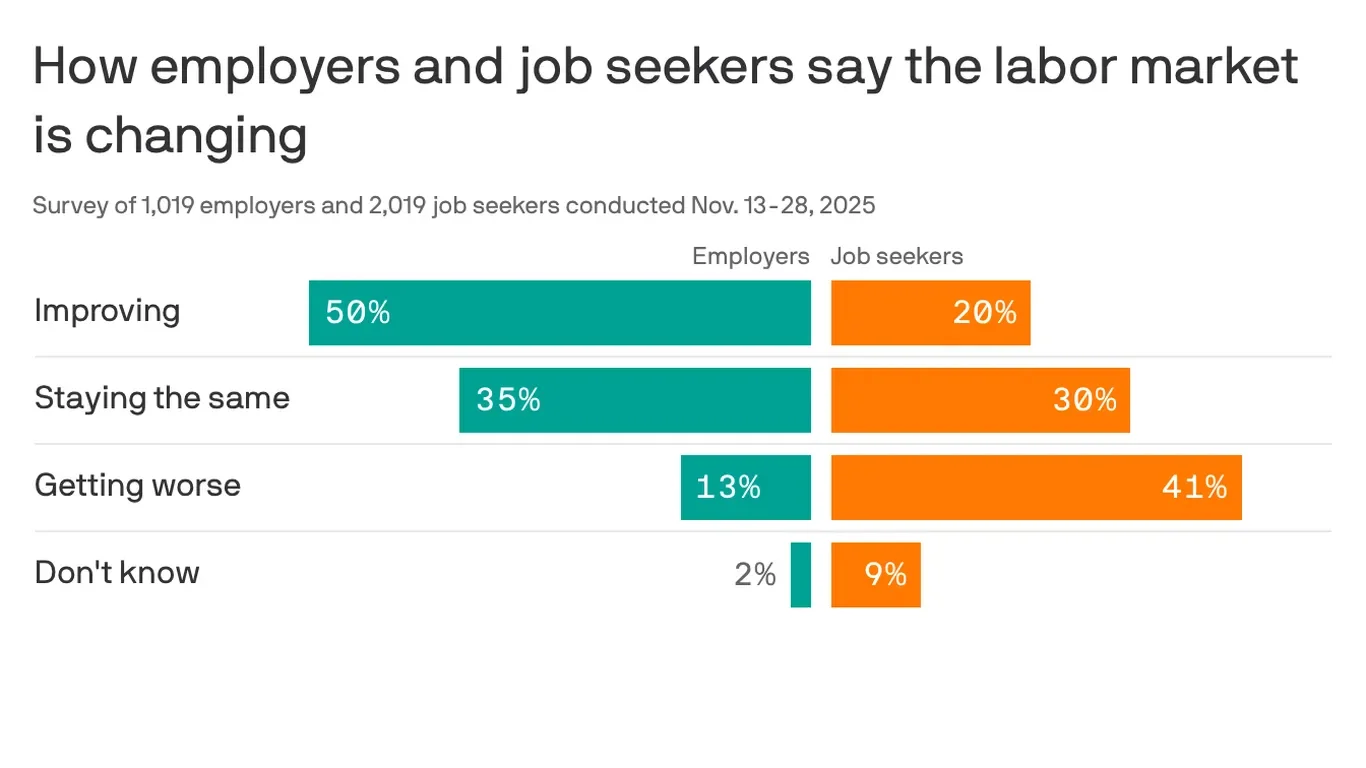
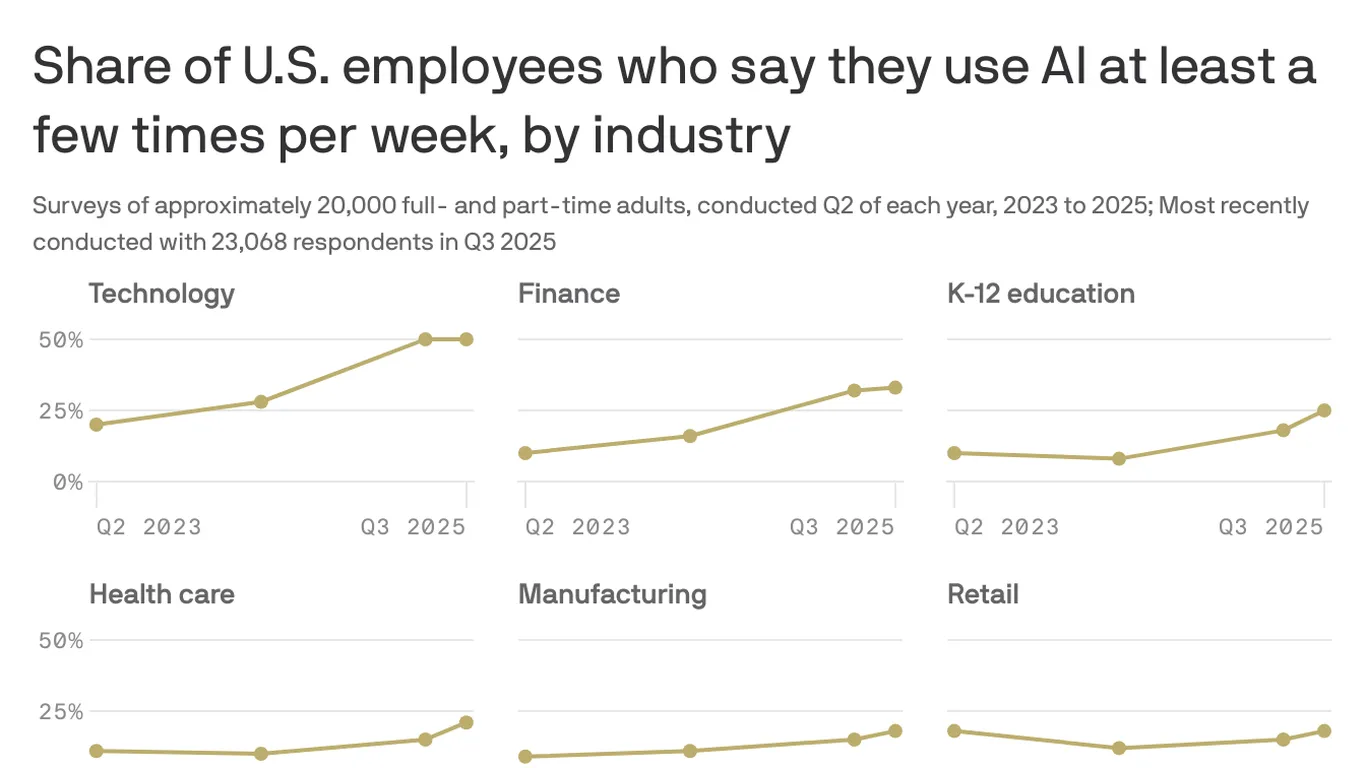
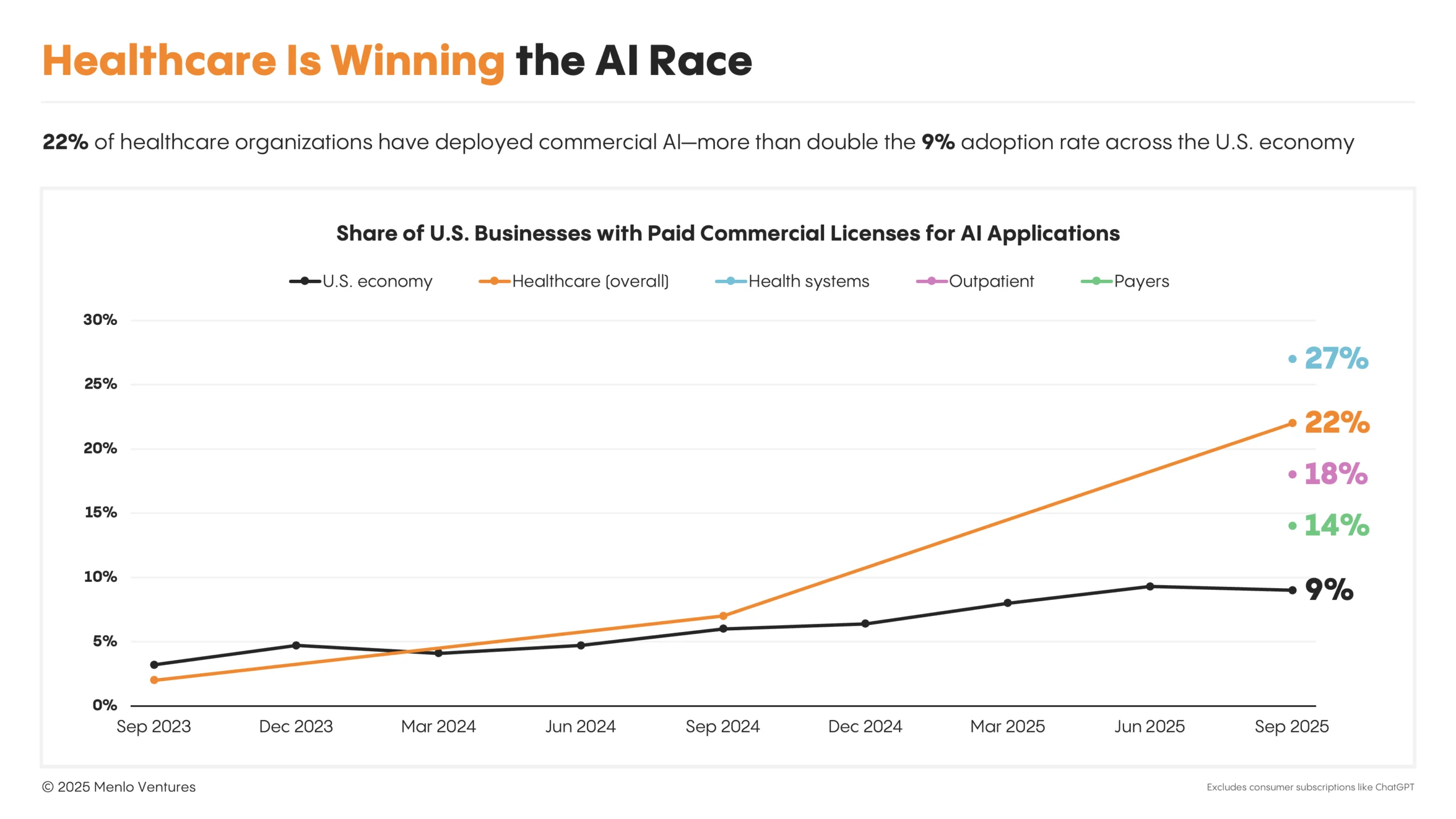
Palantir Dips as AI Adoption Hurdles and Tech Selloff Pressure PLTR
Palantir slid on Wednesday after a strong fourth‑quarter earnings beat and revenue growth, as market‑wide tech weakness and geopolitical tensions weighed on the stock; Q4 revenue rose 70% year over year to $1.407 billion with U.S. sales up 93%, though CEO Alex Karp warned that uneven AI adoption outside the U.S. could limit international growth. The shares traded beneath key moving averages, signaling bearish near‑term momentum amid a broad market pullback.