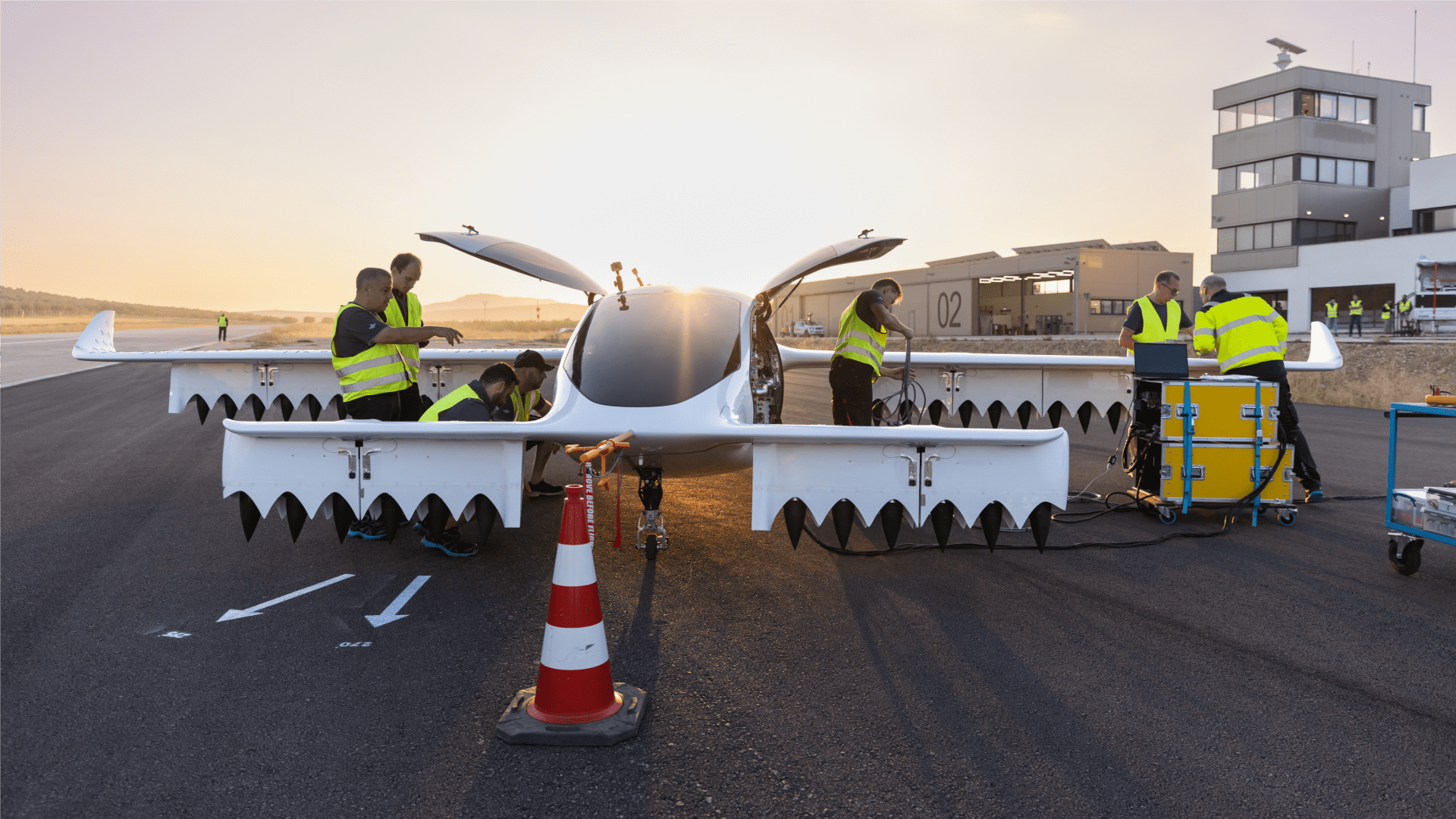
"Lilium: Revolutionizing Air Travel from the Inside Out"
German aerospace company Lilium aims to revolutionize air travel with its electric vertical take-off and landing (eVTOL) jet, targeting zero emissions and a meaningful reduction in CO2 emissions. With a successful prototype test in 2022, the company plans to enter service by 2026 and has attracted investment from Tencent and Earlybird Venture Capital. Priced at $9 million for a premium market jet and $7 million for a six-seater version, Lilium differentiates itself from competitors by focusing on regional flights and utilizing jet technology for longer range.





