Astronomers Measure Supermassive Black Hole Spinning at Quarter Light Speed
TL;DR Summary
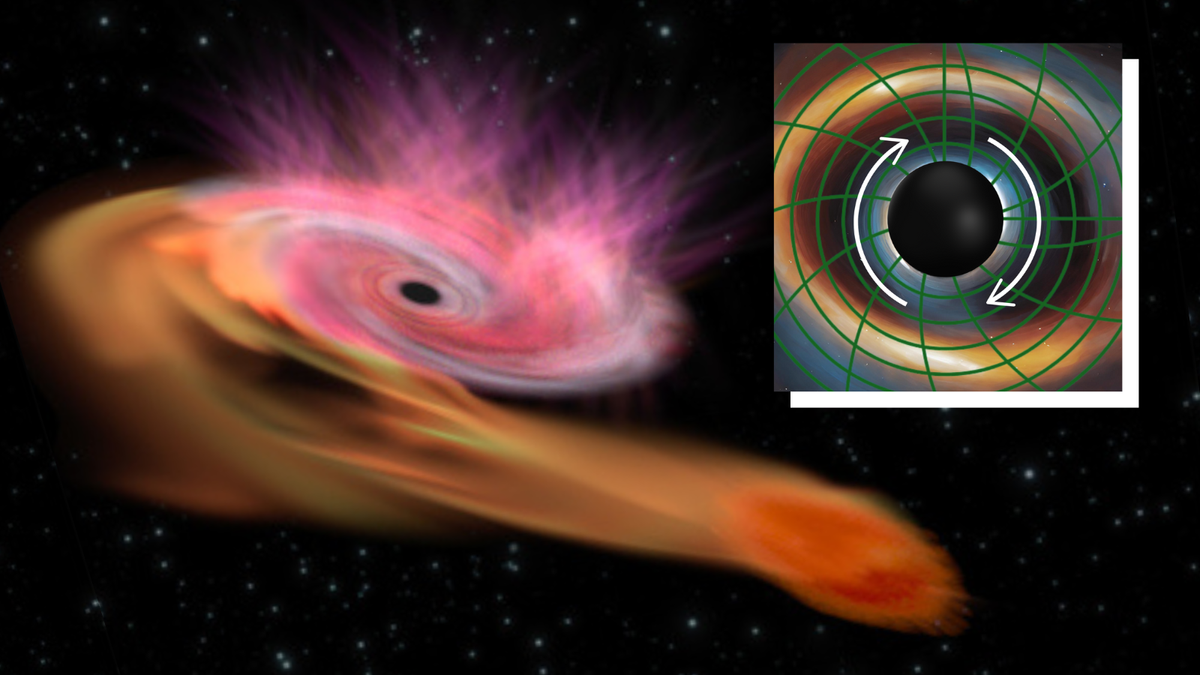
Researchers have discovered that the "wobble" of an accretion disk formed from a star ripped apart by a supermassive black hole can reveal the black hole's spin speed. This wobble, caused by the Lense-Thirring effect, was observed using NASA's NICER X-ray telescope. The findings suggest that the black hole involved in the event was spinning slower than expected, at less than 25% the speed of light. Future observations, particularly with the upcoming Vera C. Rubin Observatory, could provide more insights into the spin distribution and evolution of supermassive black holes.
- Churning spacetime and destroyed stars help reveal how fast supermassive black holes spin Space.com
- Lense–Thirring precession after a supermassive black hole disrupts a star Nature.com
- Astronomers Just Calculated The Spin Speed of a Supermassive Black Hole ScienceAlert
- Using wobbling stellar material, astronomers measure the spin of a supermassive black hole for the first time Phys.org
- Groundbreaking Measurement Reveals a Black Hole Spinning at a Quarter the Speed of Light Gizmodo
Reading Insights
Total Reads
0
Unique Readers
0
Time Saved
5 min
vs 6 min read
Condensed
92%
1,145 → 90 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Space.com