Uncovering Ancient Genetic Connections with Unprecedented Accuracy
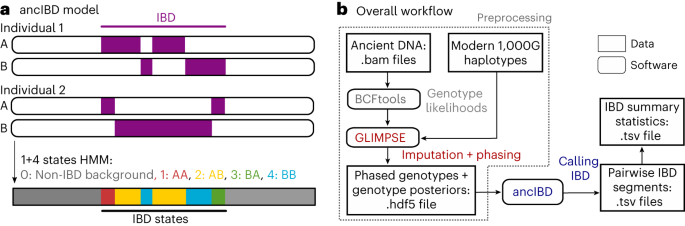
Researchers have developed a method called ancIBD to accurately detect identity-by-descent (IBD) segments in human ancient DNA (aDNA) data. IBD segments are long genomic segments that are co-inherited from a recent common ancestor and can provide valuable information about genealogical connections and demographic history. The ancIBD method utilizes phased genotype likelihoods imputed by GLIMPSE and a hidden Markov model (HMM) to infer IBD blocks. The researchers evaluated the performance of ancIBD on simulated and downsampled aDNA data, demonstrating its robustness in detecting IBD segments even at low coverage depths. They also used ancIBD to identify biological relatives and uncover genealogical connections among ancient Eurasian individuals, shedding light on ancient migration patterns and population interactions.
- Accurate detection of identity-by-descent segments in human ancient DNA Nature.com
- Revealing close and distant relatives in ancient DNA with unprecedented precision Phys.org
- Cousins in the Ancient World Harvard Magazine
- Revealing Relatives in Ancient DNA With Unprecedented Precision Technology Networks
- Shared chromosomal segments connect ancient human societies Nature.com
Reading Insights
0
6
52 min
vs 53 min read
99%
10,431 → 114 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Nature.com