NASA develops 3D-printed superalloy for extreme environments and nuclear space travel.
TL;DR Summary
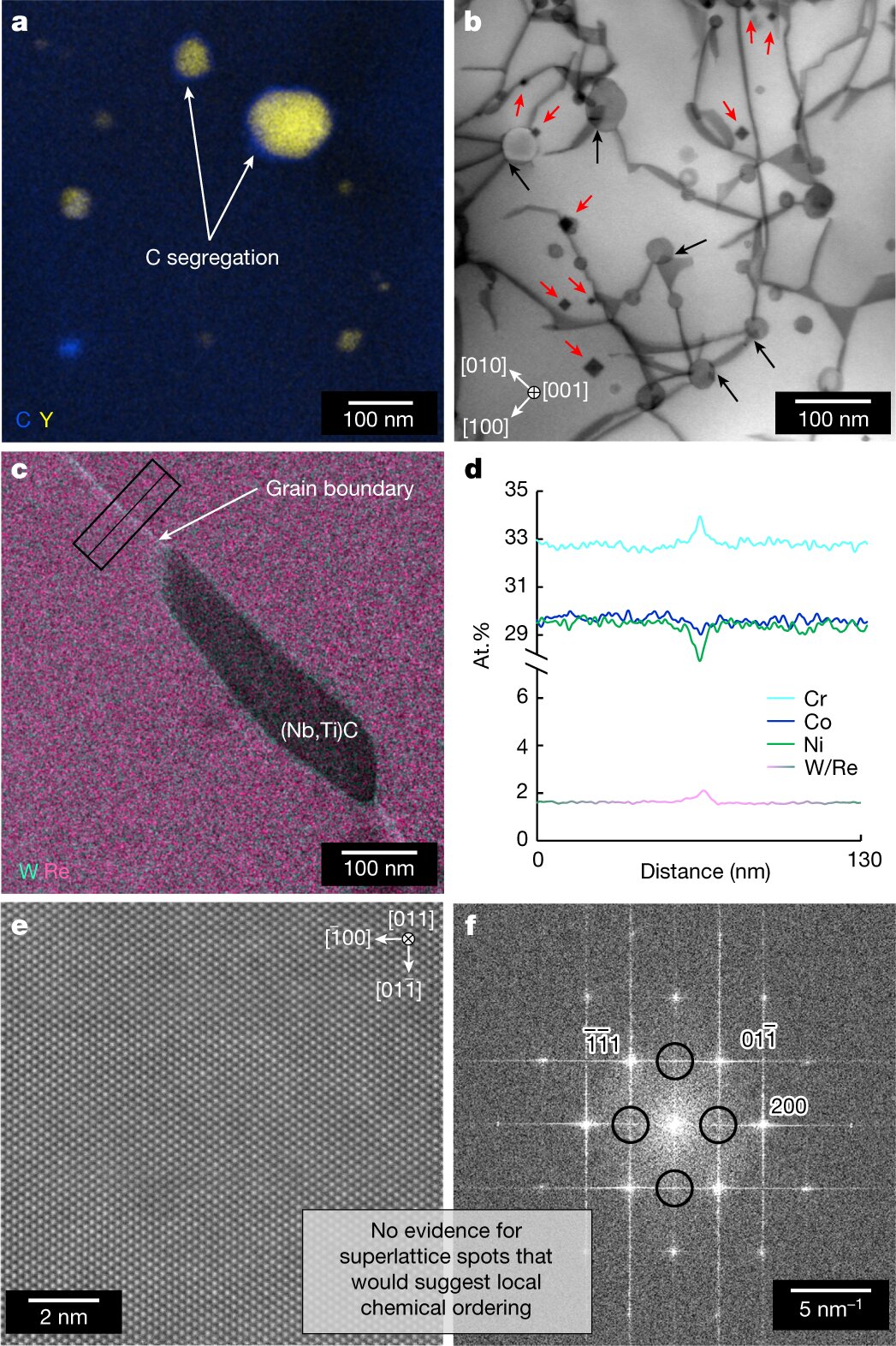
A team of materials scientists from NASA, The Ohio State University, and HX5 LLC have developed a 3D printing process that produces an alloy called GRX-810, which is much more resistant to stress than other alloys currently in use. The process involves adding a dusting of yttrium oxide powder to each layer of ink made of a mixture of cobalt, nickel, and chrome particles. The new alloy lasted for 6,500 hours in a creep test, compared to current top materials that typically last approximately 10 hours.
Reading Insights
Total Reads
0
Unique Readers
1
Time Saved
2 min
vs 3 min read
Condensed
85%
580 → 86 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Phys.org