Unveiling Dark Matter's Secrets: Exploding Axion Stars and Neutron Star Debris
TL;DR Summary
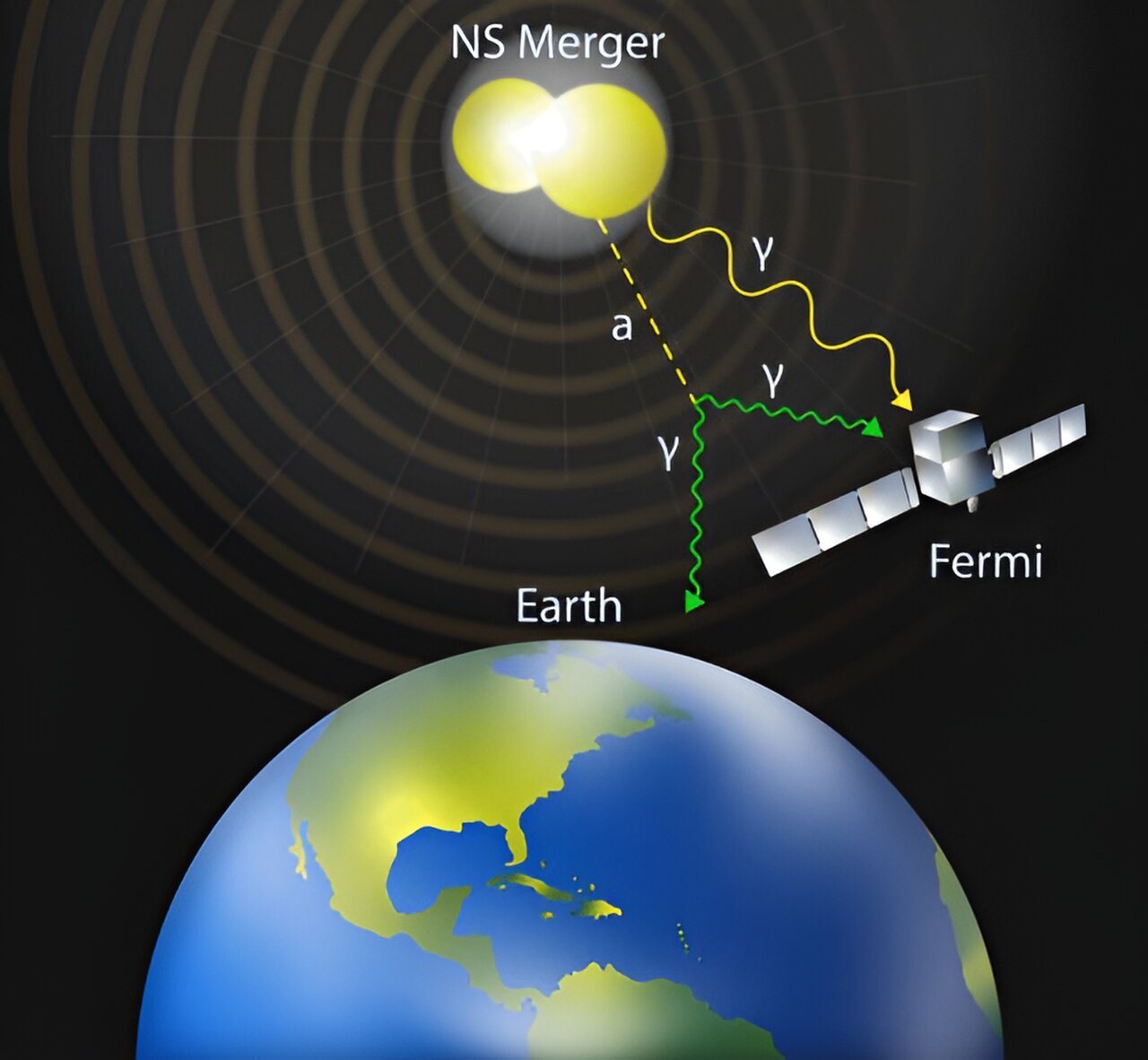
Researchers from Washington University in St. Louis have used observations from the collision of two neutron stars to derive new constraints on axion-like particles, which are leading candidates for dark matter. The study suggests that these exotic particles produced in the aftermath of neutron star mergers can escape and decay into photons, creating unique electromagnetic signals that can be detected by gamma-ray telescopes like NASA's Fermi-LAT. This research provides a new window of opportunity in the quest for understanding the missing matter in the universe and could lead to further insights into the nature of dark sector particles like axions.
Topics:science#astrophysics#axion-like-particles#dark-matter#gamma-ray-telescopes#neutron-stars#physics
- Finding new physics in debris from colliding neutron stars Phys.org
- 'Axion stars' that went boom after the Big Bang could shed light on dark matter Space.com
- Can Exploding 'Axion Stars' Help Pin Down Dark Matter? Scientific American
- King's College Scientists Near Dark Matter Discovery Mirage News
- Unlocking the Shadows: Novel Approach to Detect Dark Matter's Elusive Axions Medriva
Reading Insights
Total Reads
0
Unique Readers
5
Time Saved
3 min
vs 4 min read
Condensed
85%
678 → 100 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Phys.org