The Role of Dopamine in Reward Seeking and Risk Assessment
TL;DR Summary
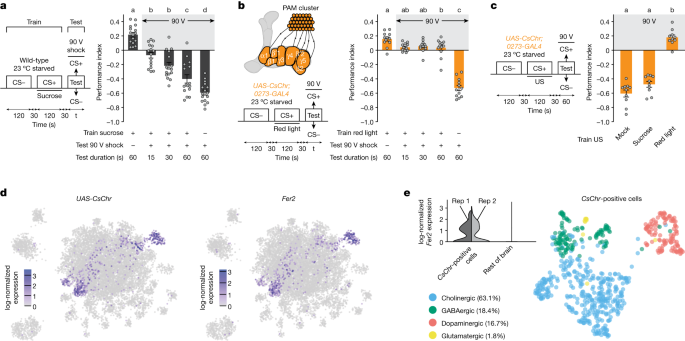
Researchers have discovered that specific dopaminergic neurons in the brains of fruit flies play a crucial role in driving reward-seeking behavior, even in the face of adverse consequences. The study found that activation of these neurons, known as β′2 and γ4 DANs, led the flies to persistently seek rewards, such as sucrose, despite being subjected to electric shocks. The findings shed light on the neural mechanisms underlying reward-seeking behavior and could have implications for understanding substance use disorders in humans.
Topics:science#adverse-consequences#dopaminergic-systems#drosophila#neural-mechanisms#neuroscience#reward-seeking
Reading Insights
Total Reads
0
Unique Readers
1
Time Saved
81 min
vs 82 min read
Condensed
100%
16,262 → 80 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Nature.com