Powerful Winds Create Spectacular Quasar-Driven Superbubbles
TL;DR Summary
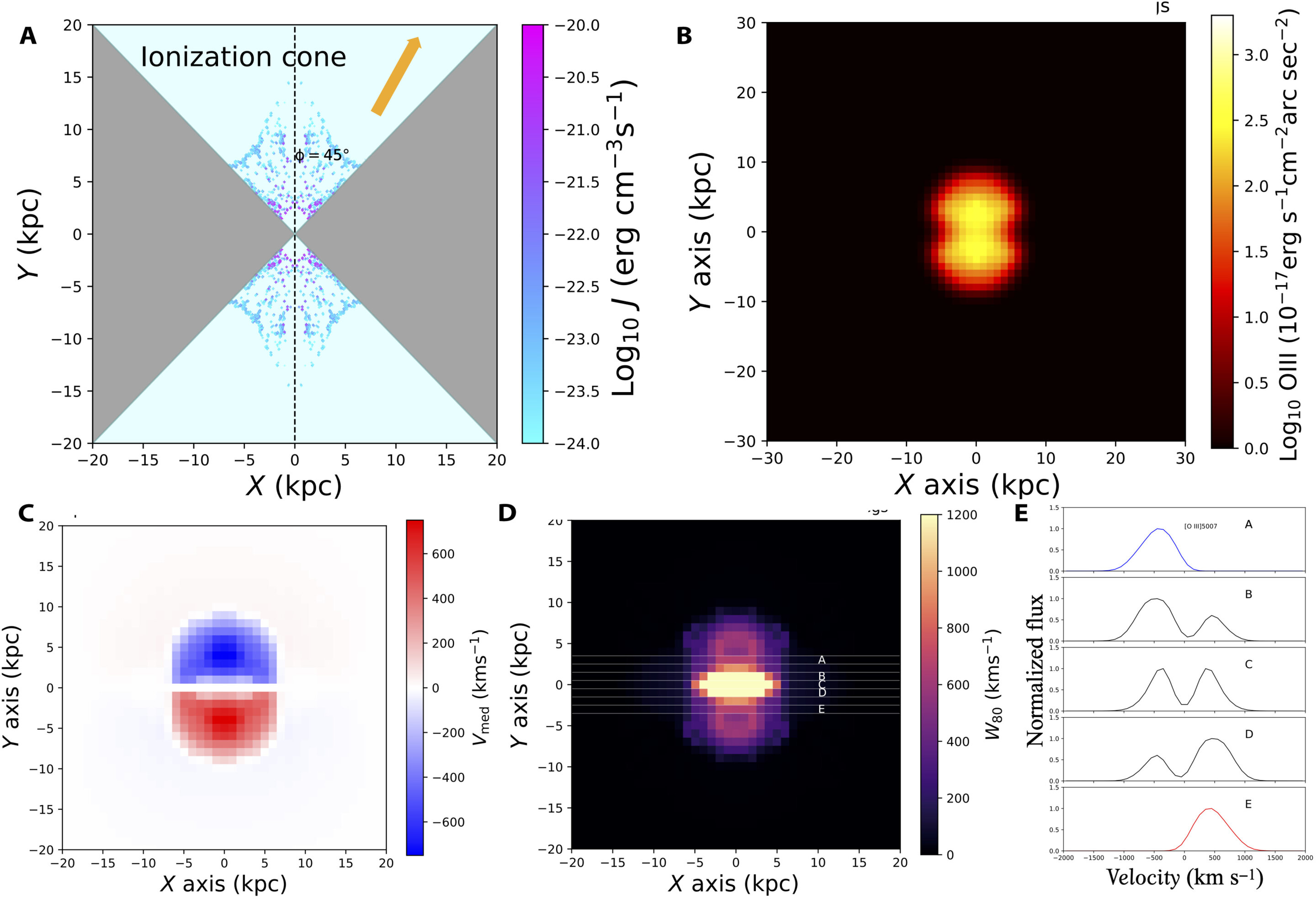
Astrophysicists have discovered ionized gas nebulae surrounding three luminous red quasars, featuring pairs of "superbubbles." Using data from the Gemini North telescope in Hawaii, the researchers found that the quasar-generated winds play a role in galaxy formation, as the superbubbles resemble the Fermi bubbles in the Milky Way. The observations and simulations suggest that these bubble structures contribute to the phase of galaxy formation where nebulae are blown from their host galaxies into a surrounding galactic halo.
Reading Insights
Total Reads
0
Unique Readers
5
Time Saved
2 min
vs 3 min read
Condensed
82%
427 → 77 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Phys.org