"Discovery of the Most Metal-Poor Extreme Helium Star by Astronomers"
TL;DR Summary
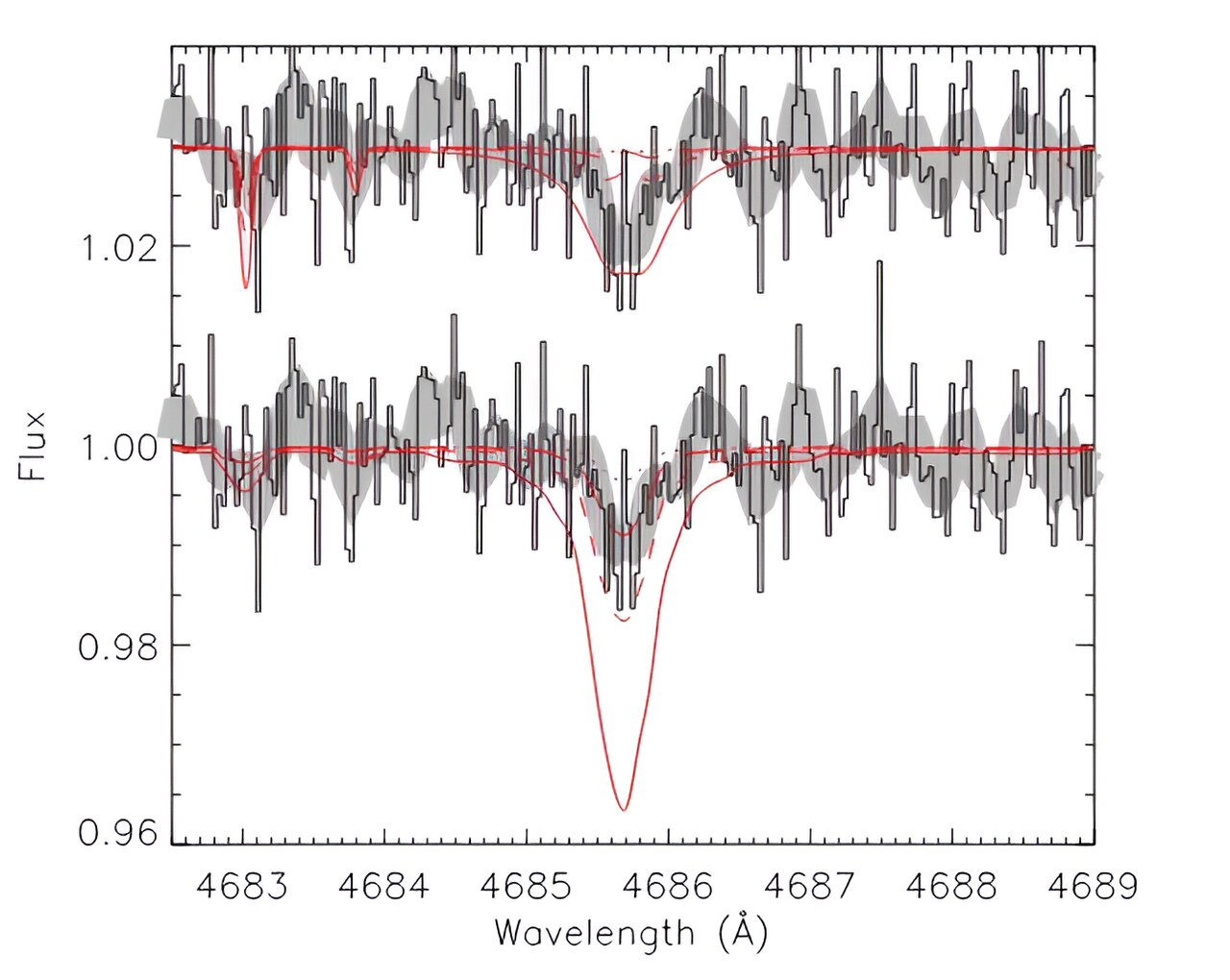
Using the Southern African Large Telescope (SALT), astronomers have discovered EC 19529−4430, the most metal-poor extreme helium star known to date, located in the Galactic halo about 15,500 light years away. The star's surface is primarily composed of carbon-nitrogen-oxygen-processed helium, and it is the coolest known carbon-poor and nitrogen-rich extreme helium star. Researchers believe it likely formed from the merger of two helium white dwarfs and will evolve into a core helium-burning EHe subdwarf.
Reading Insights
Total Reads
0
Unique Readers
8
Time Saved
2 min
vs 3 min read
Condensed
86%
525 → 74 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Phys.org