Atlas-guided transcription-factor map unlocks CD8+ T cell programming for immunotherapy
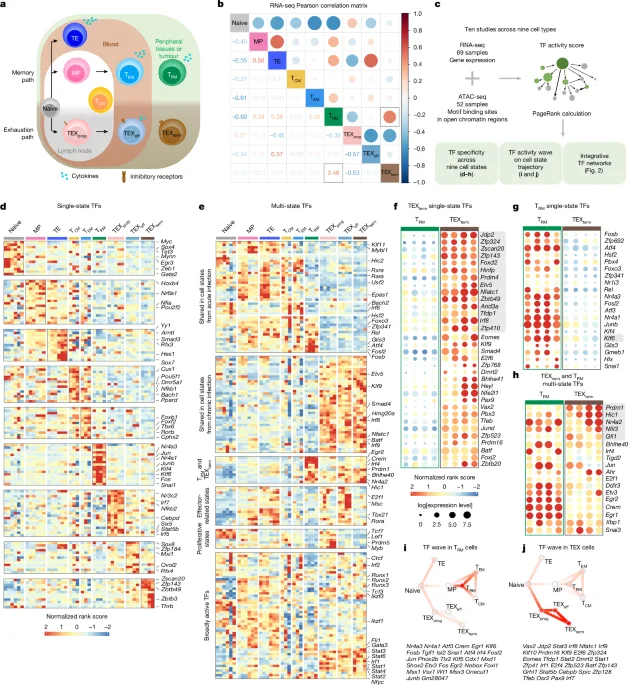
A multi-omics atlas of nine CD8+ T cell states (RNA-seq and ATAC-seq) analyzed with the Taiji network approach reveals state-selective transcription factors that drive protective tissue-resident memory (TRM) versus terminally exhausted (TEXterm) states. The study identifies new TEXterm TFs (e.g., ZSCAN20, JDP2) and shared regulators (HIC1, GFI1), maps TF–TF networks and “waves” coordinating state transitions, and uses in vivo Perturb-seq CRISPR screens to show TEXterm TFs govern exhaustion while preserving TRM formation. Deleting TEXterm-selective TFs enhances tumor control and augments immune checkpoint blockade, with human T cells showing improved effector function upon TF disruption. Overall, the Atlas enables precise engineering of T cell states to design more effective cellular immunotherapies.
- Atlas-guided discovery of transcription factors for T cell programming Nature
- A genetic blueprint for avoiding killer T cell exhaustion Medical Xpress
- Blueprints for Designing T Cells that Kill UC San Diego Today
- Could these two genes make T cells unstoppable? Salk Institute for Biological Studies
- San Diego Labs Flip T Cell Kill Switches In High-Stakes Cancer Fight Hoodline
Reading Insights
1
4
83 min
vs 84 min read
99%
16,781 → 110 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on Nature