Unlocking the Brain's Potential with Omega-3 Fatty Acids.
TL;DR Summary
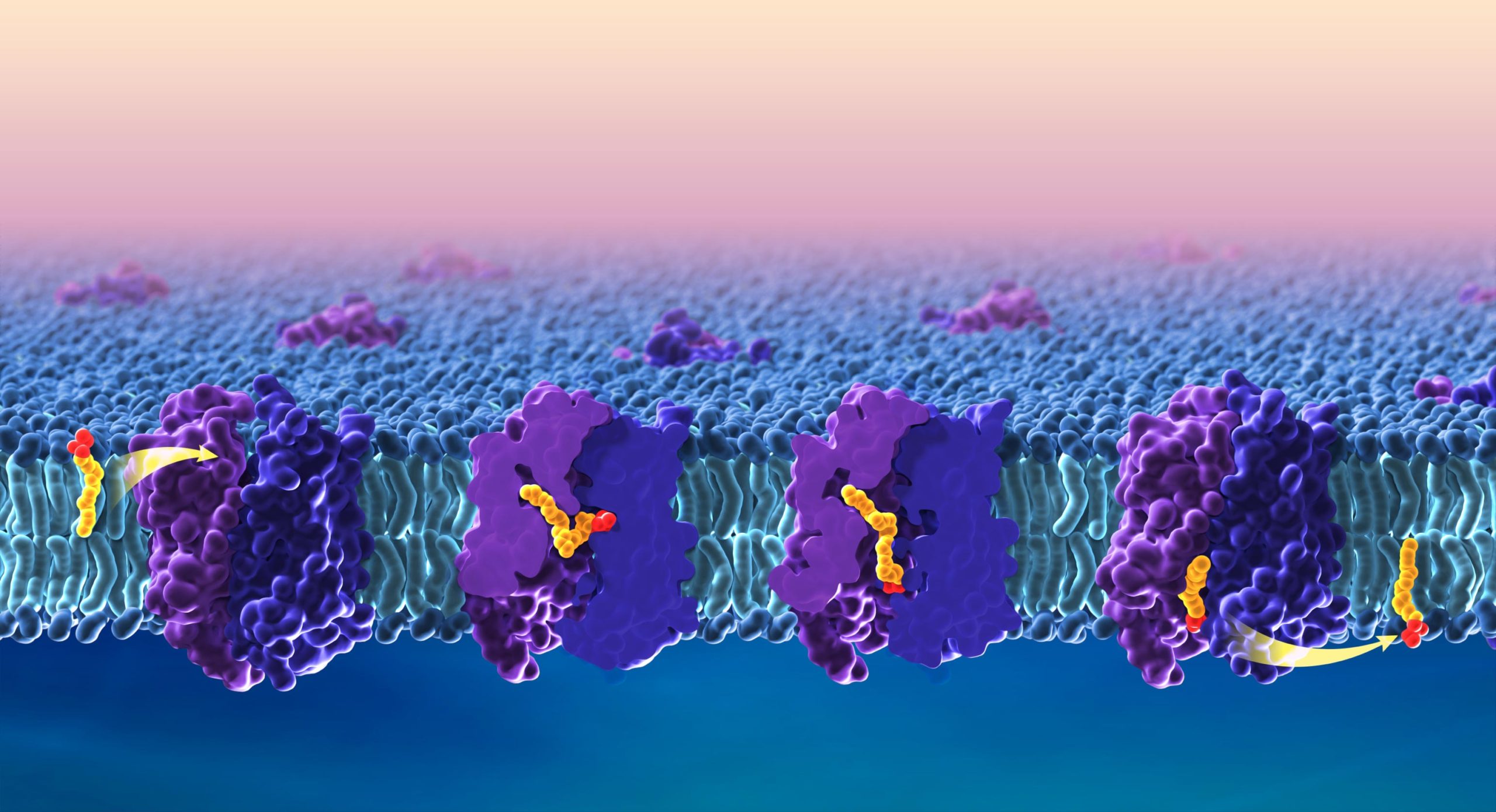
Researchers at UCLA, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, and NIH have developed a zebrafish model to study how the brain acquires essential omega-3 fatty acids, including DHA and ALA, and how they pass through the blood-brain barrier via the lipid transporter Mfsd2a. The study provides images of the structure of zebrafish Mfsd2a, which is similar to its human counterpart, and identifies three compartments in Mfsd2a that suggest distinct steps required to move and flip fatty acids through the transporter. The findings may aid in the design of targeted drug delivery into the brain and central nervous system.
Topics:health#blood-brain-barrier#drug-delivery#lipid-transport#omega-3#science-and-health#zebrafish-model
- Brain Food Unlocked: A Fishy Tale of Omega-3s and the Blood-Brain Barrier SciTechDaily
- In MS, omega-3 fatty acid transporter vital for producing myelin... Multiple Sclerosis News Today
- Researchers develop model for how the brain acquires essential omega-3 fatty acids National Institutes of Health (.gov)
Reading Insights
Total Reads
0
Unique Readers
0
Time Saved
2 min
vs 3 min read
Condensed
80%
469 → 96 words
Want the full story? Read the original article
Read on SciTechDaily