Revolutionary Hollow-Core Optical Fibers Promise Faster Internet Speeds
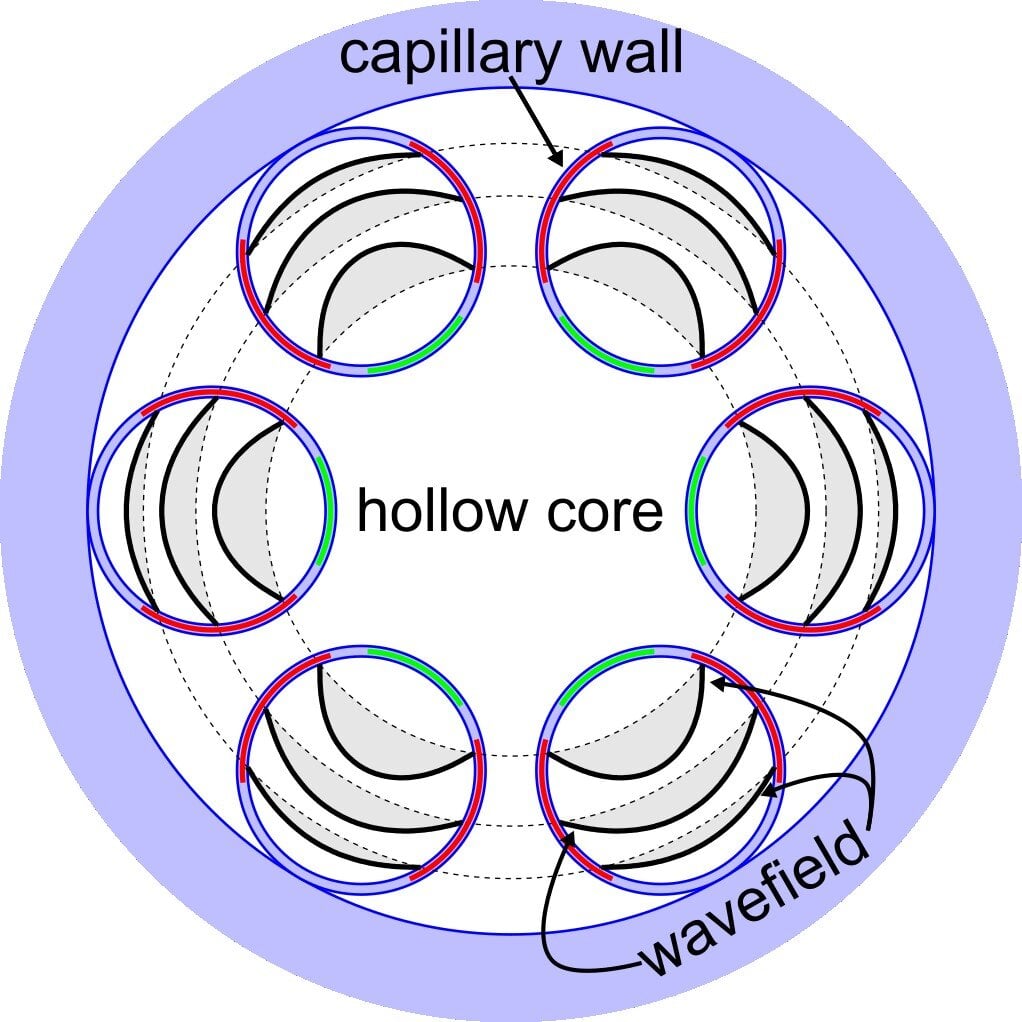
A new hollow optical fiber design using glass 'straws' could significantly increase data capacity and transmission distances, potentially leading to faster and more efficient Internet and telecommunications systems. Developed by researchers at the University of Southampton and produced by the startup Lumenisity, this innovation promises transformative improvements in data transfer speeds, especially in data centers.