Unveiling Trumpler 14's Young Low-Mass Star Population
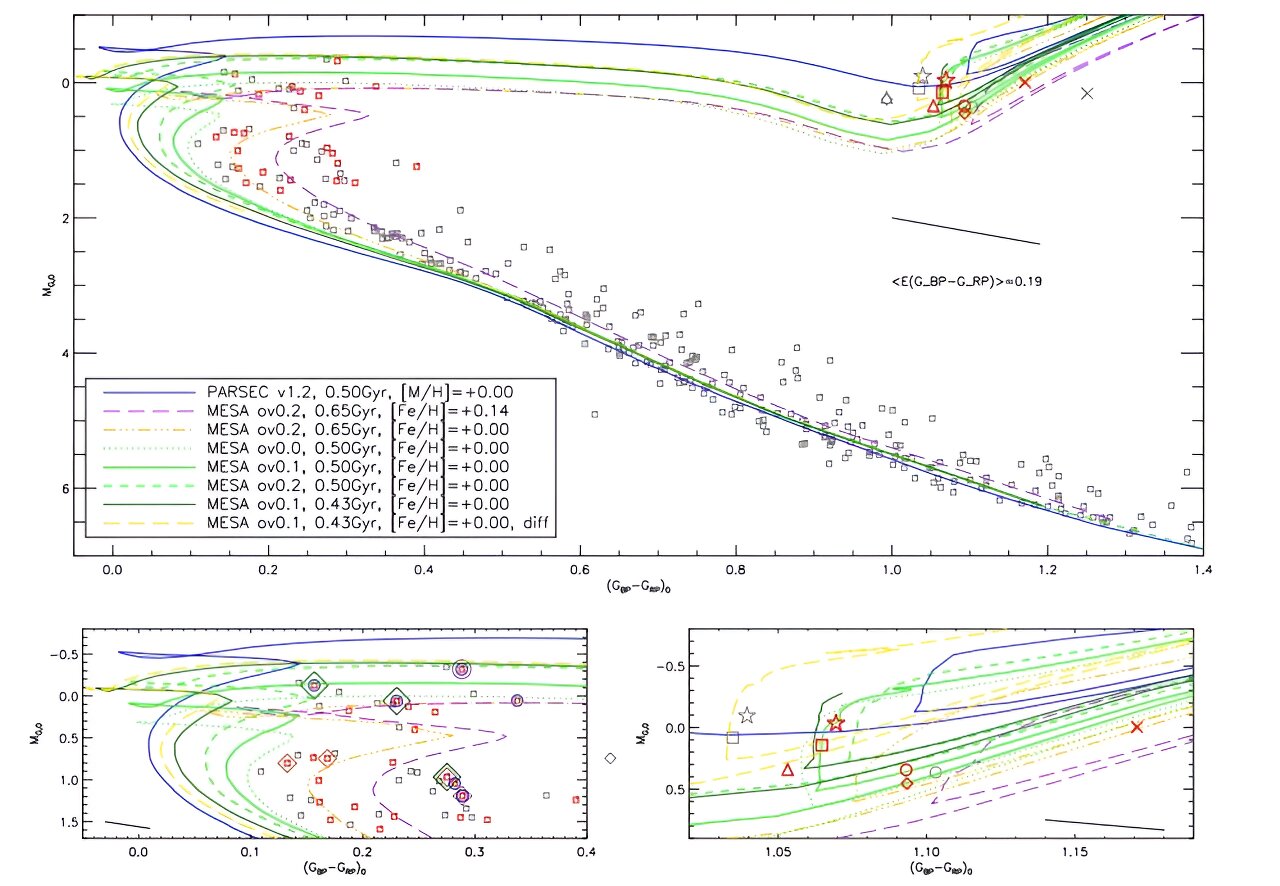
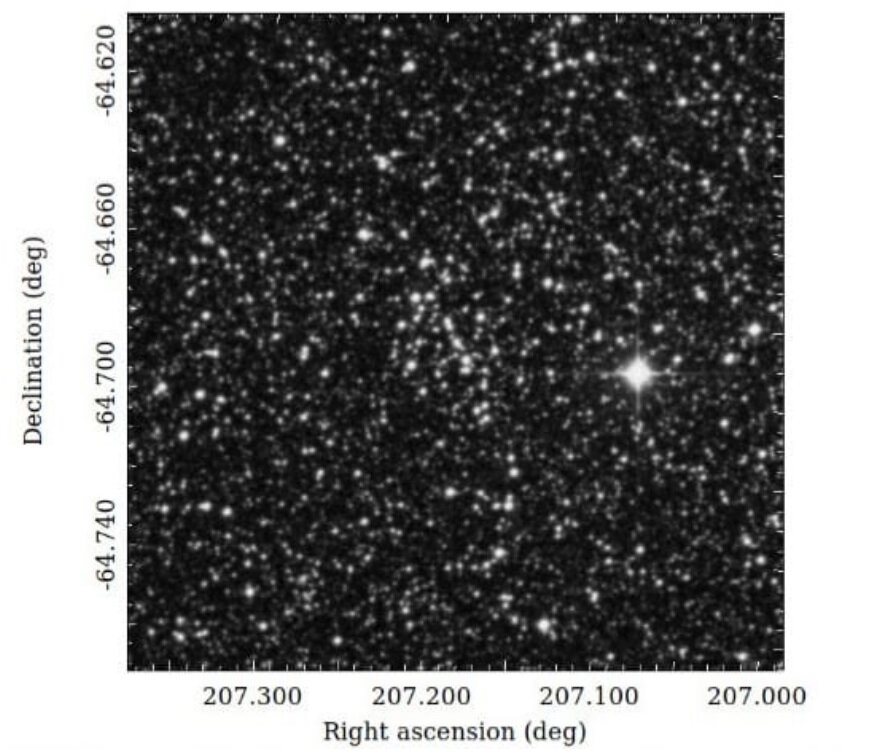
European astronomers have used the Very Large Telescope (VLT) to study the population of young low-mass stars in the open cluster Trumpler 14. Spectroscopic observations were conducted, revealing that about half of the stars in the sample have masses below 1 solar mass. The study provides valuable insights into the formation and evolution of low-mass stars in a cluster environment.